What is Zero Trust Security?
Zero Trust Security is a cybersecurity framework that operates on the principle of “never trust, always verify.” Unlike traditional perimeter-based security models that assume everything inside the network is safe, Zero Trust enforces strict identity verification for every person and device attempting to access resources, regardless of their location. It aims to minimize security risks by treating every request as a potential threat until verified.
Why is Zero Trust Security Important?
With the rapid digital transformation, the rise of remote work, and the increasing sophistication of cyber threats, traditional security models no longer suffice. Organizations face heightened risks from insider threats, lateral movement attacks, and vulnerabilities in hybrid and multi-cloud environments. Zero Trust mitigates these risks by continuously authenticating users, enforcing least privilege access, and segmenting networks to limit attack surfaces.
How Does Zero Trust Security Work?
Zero Trust is built on several core principles:
- Verify Explicitly – Authenticate and authorize access based on multiple factors, including user identity, device compliance, and location.
- Least Privilege Access – Users and devices receive only the minimum permissions required to perform their tasks, reducing exposure to potential threats.
- Micro-Segmentation – The network is divided into isolated segments to prevent lateral movement of threats, ensuring that a breach in one area does not compromise the entire system.
- Continuous Monitoring and Risk Assessment – Access requests are continuously monitored and analyzed based on risk levels, ensuring that security is adaptive to evolving threats.
- Assume Breach Mentality – Organizations operate under the assumption that breaches are inevitable, implementing measures like encryption, endpoint security, and strict logging to minimize impact.
Key Benefits of Zero Trust Security
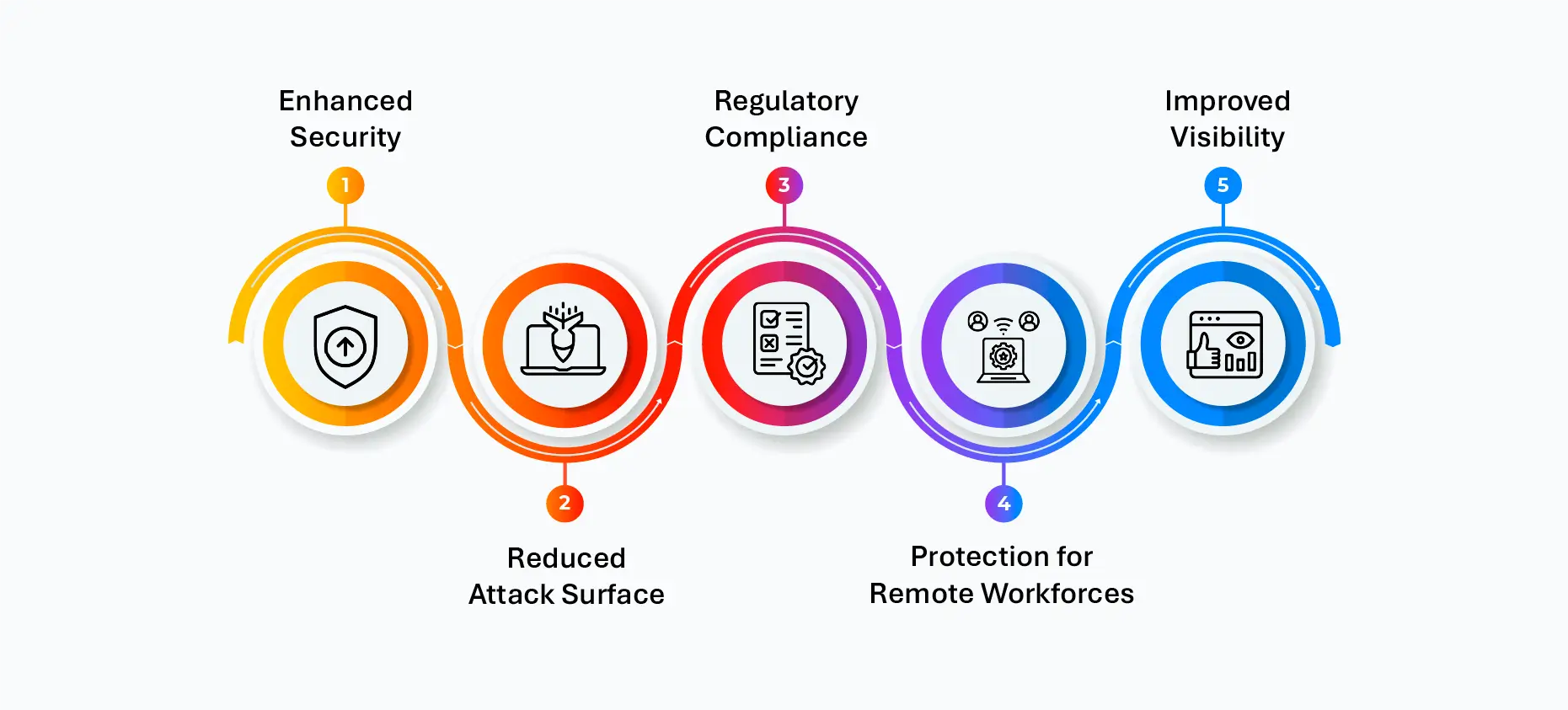
- Enhanced Security – Minimizes the risk of breaches by enforcing strict access controls.
- Reduced Attack Surface – Prevents unauthorized lateral movement across networks.
- Regulatory Compliance – Helps meet stringent data security and privacy regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA.
- Protection for Remote Workforces – Ensures secure access to enterprise resources regardless of user location.
- Improved Visibility – Provides real-time insights into user activities and potential threats.
Zero Trust vs. Traditional Security Models
Traditional security models rely on a perimeter-based approach, assuming trust for users and devices inside the network. However, this approach becomes ineffective with cloud adoption, mobile workforces, and sophisticated cyberattacks. Zero Trust, on the other hand, eliminates implicit trust and requires verification at every step, ensuring better protection against modern threats.
Challenges in Implementing Zero Trust
- Integration Complexity – Organizations may struggle to integrate Zero Trust with existing IT infrastructure.
- User Experience – Frequent authentication requests can impact productivity if not implemented seamlessly.
- Costs and Resources – Initial deployment may require significant investment in tools, automation, and training.
- Cultural Shift – Employees and IT teams need to adapt to a security-first mindset.
Zero Trust in Action: Real-World Use Cases
- Financial Services – Banks and fintech firms use Zero Trust to protect sensitive customer data and prevent fraud.
- Healthcare – Ensures compliance with HIPAA by securing patient records and limiting access based on user roles.
- Government & Defense – Strengthens national security by preventing cyber-espionage and insider threats.
- Enterprises & Cloud Security – Protects hybrid and multi-cloud environments from unauthorized access and data breaches.
Future of Zero Trust Security
As cyber threats continue to evolve, Zero Trust is becoming a cornerstone of modern cybersecurity strategies. The rise of AI-driven threat detection, automation, and policy enforcement will further enhance Zero Trust implementation. Enterprises are expected to adopt a more dynamic and adaptive approach, leveraging Zero Trust to create a resilient security posture in an increasingly digital world.
Zero Trust Security is no longer a luxury but a necessity in today’s cybersecurity landscape. By eliminating implicit trust and enforcing rigorous access controls, organizations can mitigate risks, safeguard sensitive data, and ensure compliance. As cyber threats grow more sophisticated, adopting a Zero Trust approach will be essential for achieving a robust, future-proof security framework.
Getting Started with Data Dynamics:
- Learn about Unstructured Data Management
- Schedule a demo with our team
- Read the latest blog: The CISO’s New Mandate: Governing Internal Data Policies to Defend Against AI-Powered Threats in 2025






