What is Privacy by Design?
Privacy by Design (PbD) is a foundational engineering and governance framework that integrates privacy principles directly into the design and architecture of IT systems, applications, data workflows, and operational processes. Instead of bolting on privacy controls post-deployment, PbD requires organizations to embed data protection measures from the ground up—across the entire data lifecycle.
This includes the application of data minimization techniques, anonymization and pseudonymization, contextual consent mechanisms, policy-based access control, and secure-by-default architecture. Whether building a mobile app, configuring a cloud data lake, or developing AI models, Privacy by Design ensures that privacy isn’t an afterthought—it’s an architectural standard.
Why It Matters More Than Ever
The modern data ecosystem is borderless, high-velocity, and AI-powered. Every interaction—whether through IoT devices, mobile platforms, or SaaS applications—leaves a trail of personal data. At the same time, regulatory frameworks like the GDPR, CPRA, and India’s DPDP Act are expanding in both scope and enforcement.
According to McKinsey, 71% of consumers say they would stop doing business with a company if it gave away sensitive data without permission. And Gartner predicts that by 2026, organizations that fully adopt Privacy by Design will suffer 50% fewer privacy-related breaches than those that don’t.
In a world where data breaches average $4.88 million in cost (IBM 2024), Privacy by Design isn’t just compliance—it’s cyber-resilience.
Core Principles of Privacy by Design
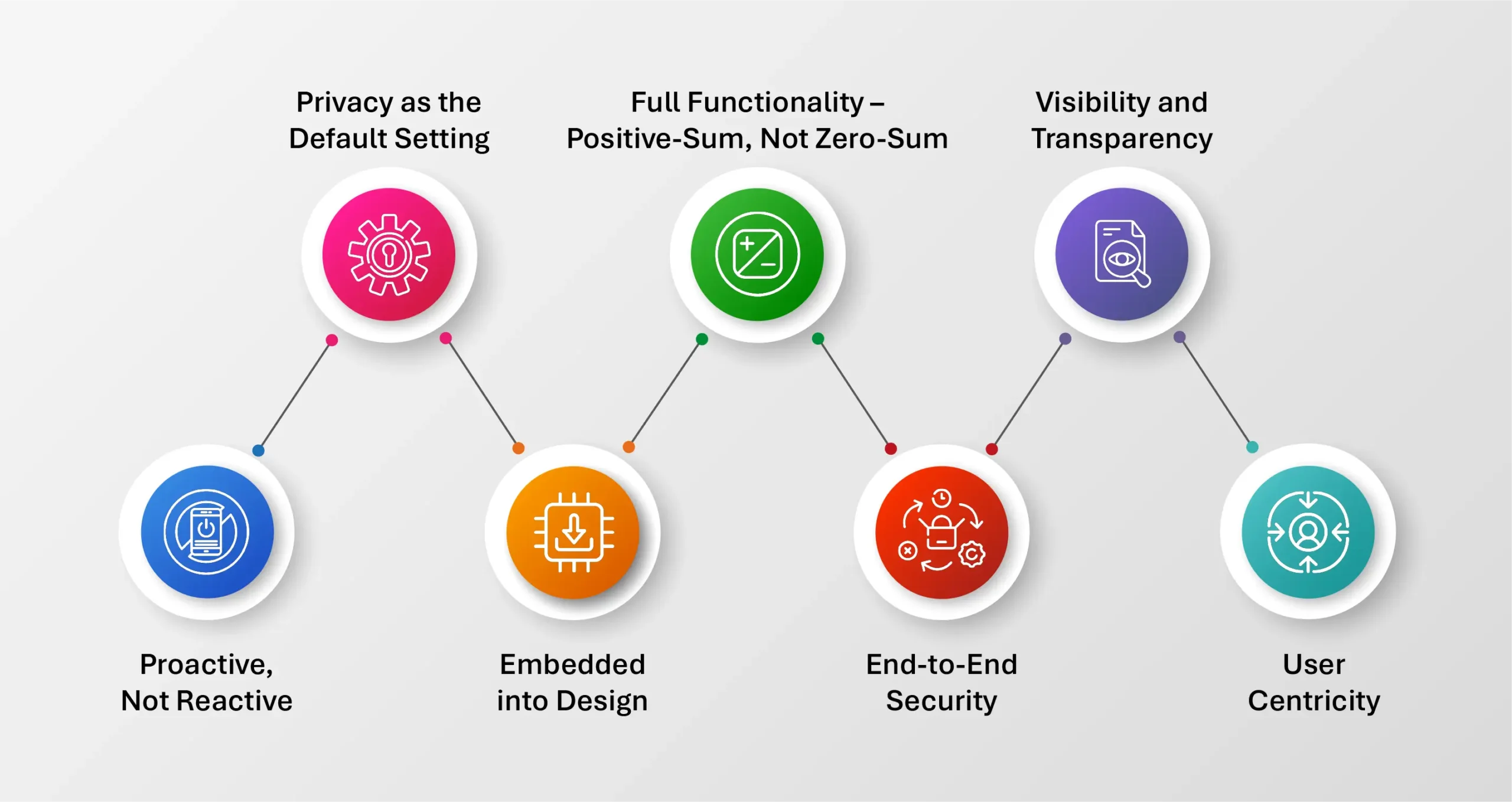
- Proactive, Not Reactive: Implement continuous privacy risk assessment engines that scan for policy violations, shadow data, or misconfigured permissions in real time.
- Privacy as the Default Setting: Configure data pipelines to automatically restrict collection to fields necessary for the intended purpose (data minimization). Ensure default retention policies delete unnecessary data after a specified lifecycle.
- Embedded into Design: During software development, embed privacy checks into CI/CD pipelines using automated code scanners that flag hardcoded credentials, exposed APIs, or unencrypted storage endpoints.
- Full Functionality – Positive-Sum, Not Zero-Sum: Design systems that enable analytics on de-identified or tokenized datasets using techniques like differential privacy, so organizations don’t have to trade utility for privacy.
- End-to-End Security: Apply transport-layer and at-rest encryption, enforce multi-factor authentication (MFA), and integrate role-based access controls (RBAC) into backend systems.
- Visibility and Transparency: Use data observability platforms that allow users to trace how their data flows across systems. Maintain real-time audit logs accessible to DPOs and compliance teams.
- User-Centricity: Develop consent orchestration workflows that are granular, revocable, and logged. Offer real-time dashboards to users showing what data is collected, where it’s used, and who it’s shared with.
Why Organizations Can’t Ignore It
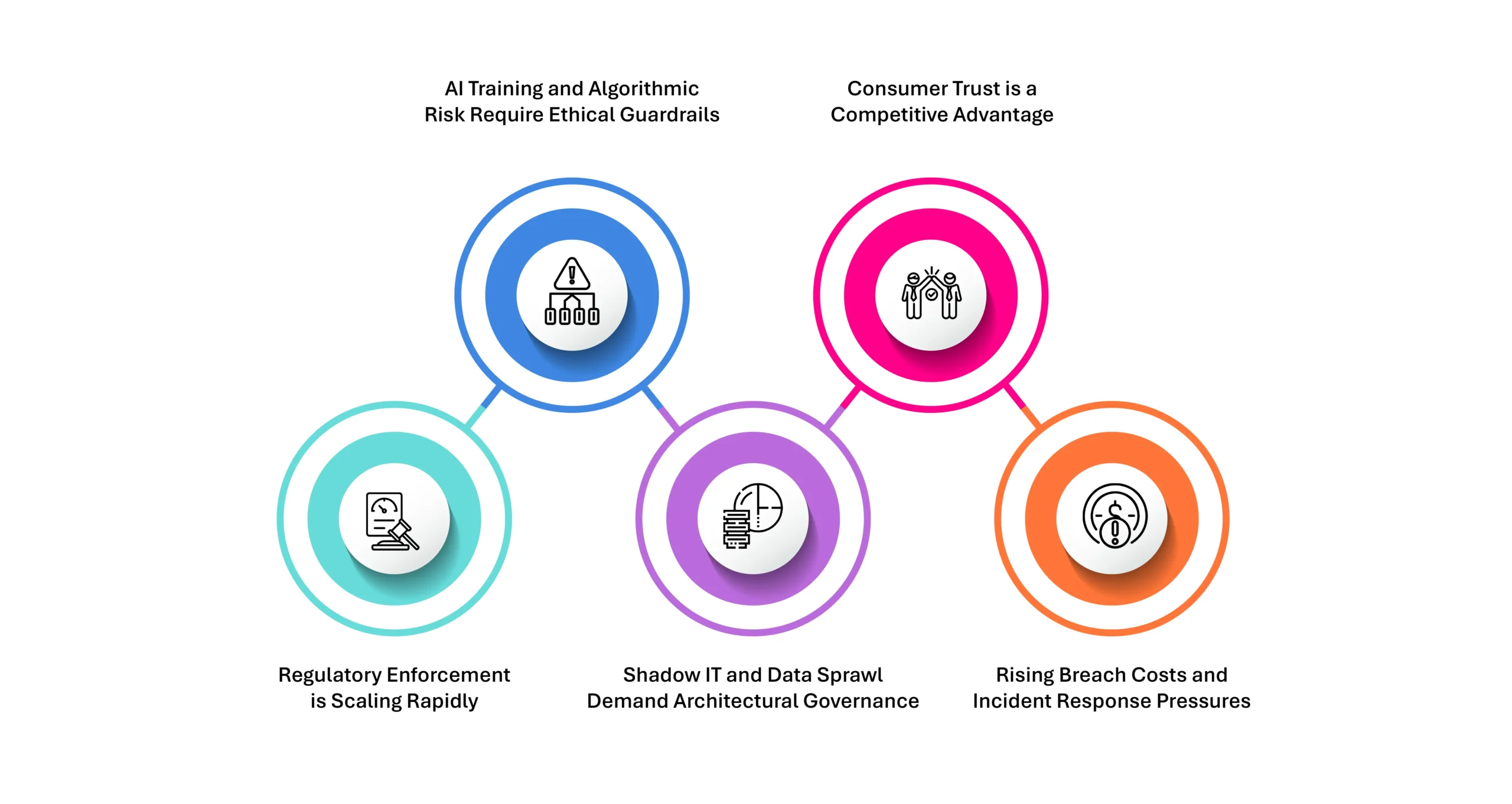
The business case for Privacy by Design goes far beyond compliance—it’s about operational readiness, reputational defense, and future-proofing your data strategy.
1. Regulatory Enforcement is Scaling Rapidly: Global privacy laws are tightening, and enforcement mechanisms are becoming more aggressive. In just the last three years, over $4 billion in GDPR fines have been levied. The proposed American Data Privacy and Protection Act (ADPPA) and India’s DPDP Act mandate demonstrable evidence of privacy controls, making PbD a legal obligation, not a best practice.
Data controllers must prove through logs, design documentation, and architecture reviews that privacy was considered at each development phase. This requires traceable audit trails, data mapping tools, and configuration management databases (CMDBs) that link data flows to privacy policies.
2. AI Training and Algorithmic Risk Require Ethical Guardrails: Enterprises deploying AI are increasingly facing scrutiny for using sensitive personal data in model training without proper consent or safeguards. Without PbD, models can inadvertently absorb and reinforce bias, discrimination, or privacy violations.
PbD calls for pre-training data audits, AI model explainability layers, and anonymization filters to ensure only privacy-compliant data feeds machine learning models.
3. Shadow IT and Data Sprawl Demand Architectural Governance: With over 67% of employees using unsanctioned SaaS tools, uncontrolled data replication and shadow access are rampant. Without embedded privacy policies, organizations lose visibility and control over who accesses sensitive data and where it is stored.
Implement centralized data governance policies with federated enforcement across systems. Use metadata analytics to detect unauthorized data copies and apply policy-driven repermissioning.
4. Consumer Trust is a Competitive Advantage: As digital trust becomes a critical market differentiator, customers expect transparency, control, and ethical usage of their data. Brands that embed privacy into every layer of user interaction—right down to cookie banners and opt-in flows—build long-term loyalty and resilience against reputational damage.
PbD systems should integrate with customer identity and access management (CIAM) tools to offer privacy self-service portals, opt-out APIs, and customizable data sharing preferences.
5. Rising Breach Costs and Incident Response Pressures: The average time to identify a data breach is 204 days. With privacy violations increasingly tied to financial penalties, incident response must evolve from reactive patchwork to pre-emptive defense.
Design breach containment workflows using automated triggers. If sensitive data is exposed, built-in tagging and access controls can help isolate affected systems, notify authorities, and limit the blast radius.
Privacy by Design isn’t just a legal framework—it’s the foundation of modern digital ethics. It enables enterprises to innovate without compromising trust, comply without slowing down, and build infrastructure that respects the rights of individuals at every layer. As AI, cloud, and cyber threats converge, one thing is clear: the future belongs to businesses that don’t just process data, but protect it by design.
Getting Started with Data Dynamics:
- Learn about Unstructured Data Management
- Schedule a demo with our team
- Read the latest blog: AI Is Only as Secure as the Data You Feed It. Is Yours Truly Ready?






