What is Infrastructure Optimization?
Infrastructure Optimization is the continuous process of analyzing, modernizing, and aligning an organization’s IT infrastructure to ensure peak performance, cost efficiency, scalability, and sustainability. It involves fine-tuning the entire technology stack—compute, storage, network, and applications—to reduce waste, improve agility, and support evolving business needs.
In today’s digital-first world, where cloud-native applications, AI workloads, and real-time data processing are becoming the norm, infrastructure can no longer be static or overprovisioned. Optimization is no longer a one-time project—it’s a strategic mandate.
Why Infrastructure Optimization Matters Today
The explosion of unstructured data, rising cybersecurity threats, and mounting regulatory pressures are forcing enterprises to rethink their infrastructure from the ground up. According to Gartner, 60% of IT leaders plan to consolidate infrastructure across on-prem, cloud, and edge environments by 2026 to reduce complexity and drive efficiency.
Meanwhile, ESG goals and energy costs are pushing organizations to move beyond performance metrics to optimize for carbon footprint and sustainability.
In this context, Infrastructure Optimization is not just about saving resources—it’s about transforming infrastructure into a strategic enabler of secure, compliant, and innovation-ready operations.
Key Components of Infrastructure Optimization
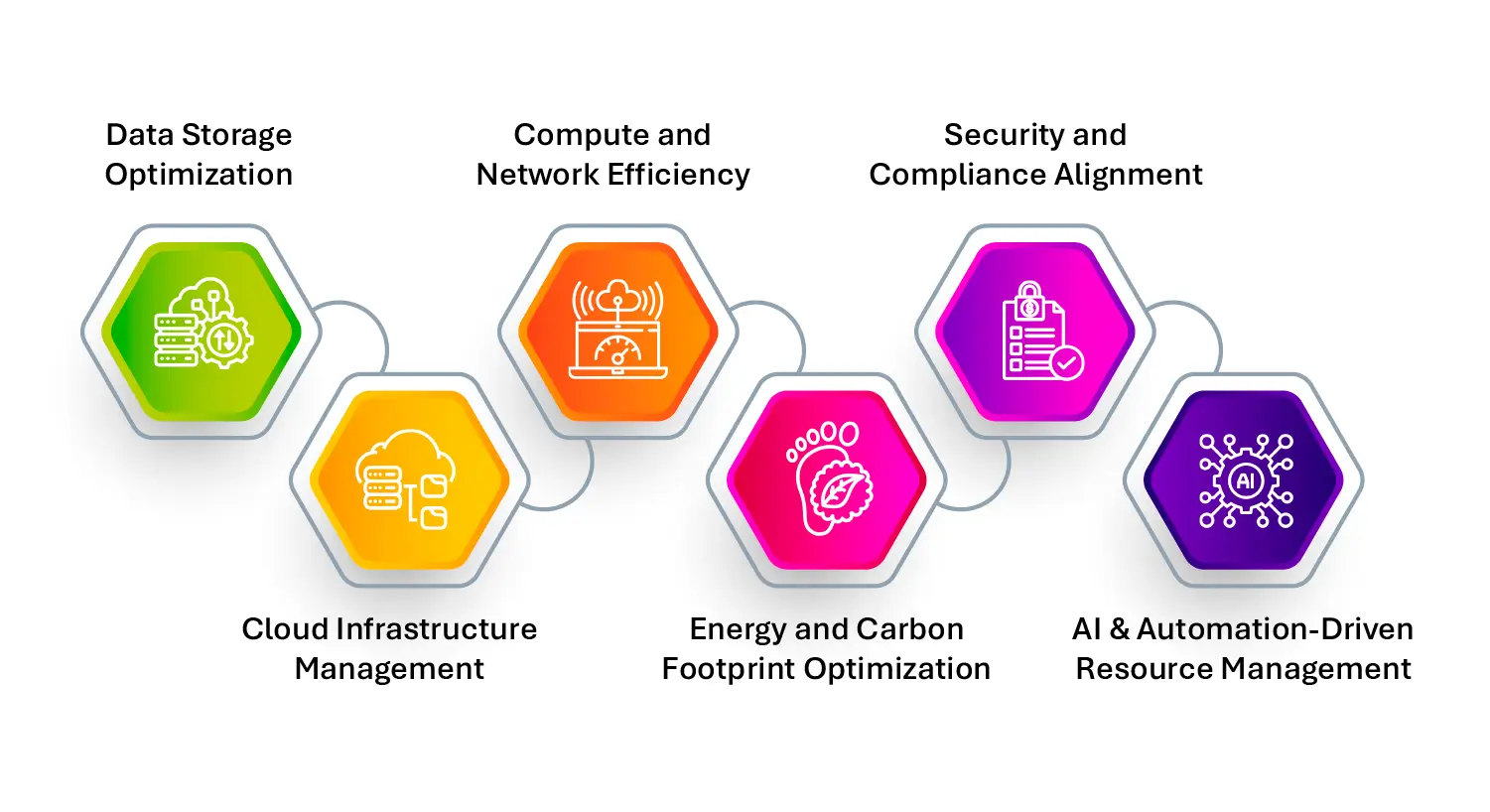
- Data Storage Optimization: Analyze storage usage patterns to identify redundant, obsolete, or trivial (ROT) data. Re-tier or archive to free up high-performance resources and cut storage costs.
- Cloud Infrastructure Management: Optimize hybrid and multi-cloud deployments through intelligent workload placement, rightsizing of instances, and automated scaling.
- Compute and Network Efficiency: Streamline compute resources by identifying idle VMs or overprovisioned containers. Optimize network bandwidth by monitoring latency and traffic bottlenecks.
- Energy and Carbon Footprint Optimization: Align infrastructure usage with energy efficiency targets. Use data heatmaps to power down unused resources and transition to green data centers.
- Security and Compliance Alignment: Integrate optimization with Data Security Posture Management (DSPM) to minimize risk exposure from unmonitored or shadow infrastructure.
- AI & Automation-Driven Resource Management: Leverage machine learning to dynamically analyze usage, forecast demand, and auto-adjust infrastructure configurations.
Benefits of Infrastructure Optimization

- Reduced Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Cut unnecessary resource usage, licensing costs, and operational overhead by maintaining lean and fit-for-purpose infrastructure.
- Increased Agility and Resilience: Enable faster response to demand spikes, application rollouts, and disaster scenarios with scalable, flexible infrastructure.
- Enhanced Security and Risk Posture: Eliminate visibility gaps by mapping and monitoring every infrastructure component, especially in hybrid and multi-cloud setups.
- Sustainability and ESG Impact: Reduce carbon emissions by decommissioning underused infrastructure and shifting workloads to energy-efficient environments.
- Better AI and Data Readiness: Ensure your infrastructure can support real-time analytics, federated data governance, and ethical AI at scale.
Infrastructure Optimization is no longer about squeezing costs. It’s about building the digital backbone for sustainable growth, AI adoption, and cyber-resilient operations. With the right analytics, automation, and governance, organizations can turn infrastructure into a source of competitive advantage—one that’s agile, intelligent, and aligned with tomorrow’s priorities.
Getting Started with Data Dynamics:
- Learn about Unstructured Data Management
- Schedule a demo with our team
- Read the latest blog: AI Is Only as Secure as the Data You Feed It. Is Yours Truly Ready?






