What is Data Tiering?
Data tiering is the practice of categorizing and storing data across different storage layers based on access frequency, value, and compliance requirements. As businesses accumulate massive amounts of structured and unstructured data, efficient tiered data storage becomes crucial for cloud storage optimization, cost savings, and regulatory adherence.
With the rise of hybrid cloud storage, organizations are adopting cloud data tiering strategies that automatically classify and move data between hot, warm, and cold storage tiers. This ensures frequently accessed data remains in high-performance storage, while inactive data is archived in low-cost, long-term storage solutions. By implementing cloud tiering solutions, businesses can achieve storage cost reduction while maintaining data accessibility and security.
Why is Data Tiering Important?
As data volumes skyrocket, enterprises face increasing pressure to optimize storage infrastructure, control costs, and ensure compliance with data protection regulations. Traditional one-size-fits-all storage models lead to excessive expenses, inefficient data access, and compliance risks. Without effective data tiering, organizations struggle with:
- High cloud storage costs due to inefficient data placement
- Slow performance when inactive data clogs high-speed storage systems
- Security and compliance risks when sensitive data is stored improperly
- Limited scalability as data demands grow exponentially
By implementing intelligent data management and best practices for cloud data tiering, businesses can maximize storage efficiency, ensure regulatory compliance, and reduce operational costs.
Key Components of Data Tiering
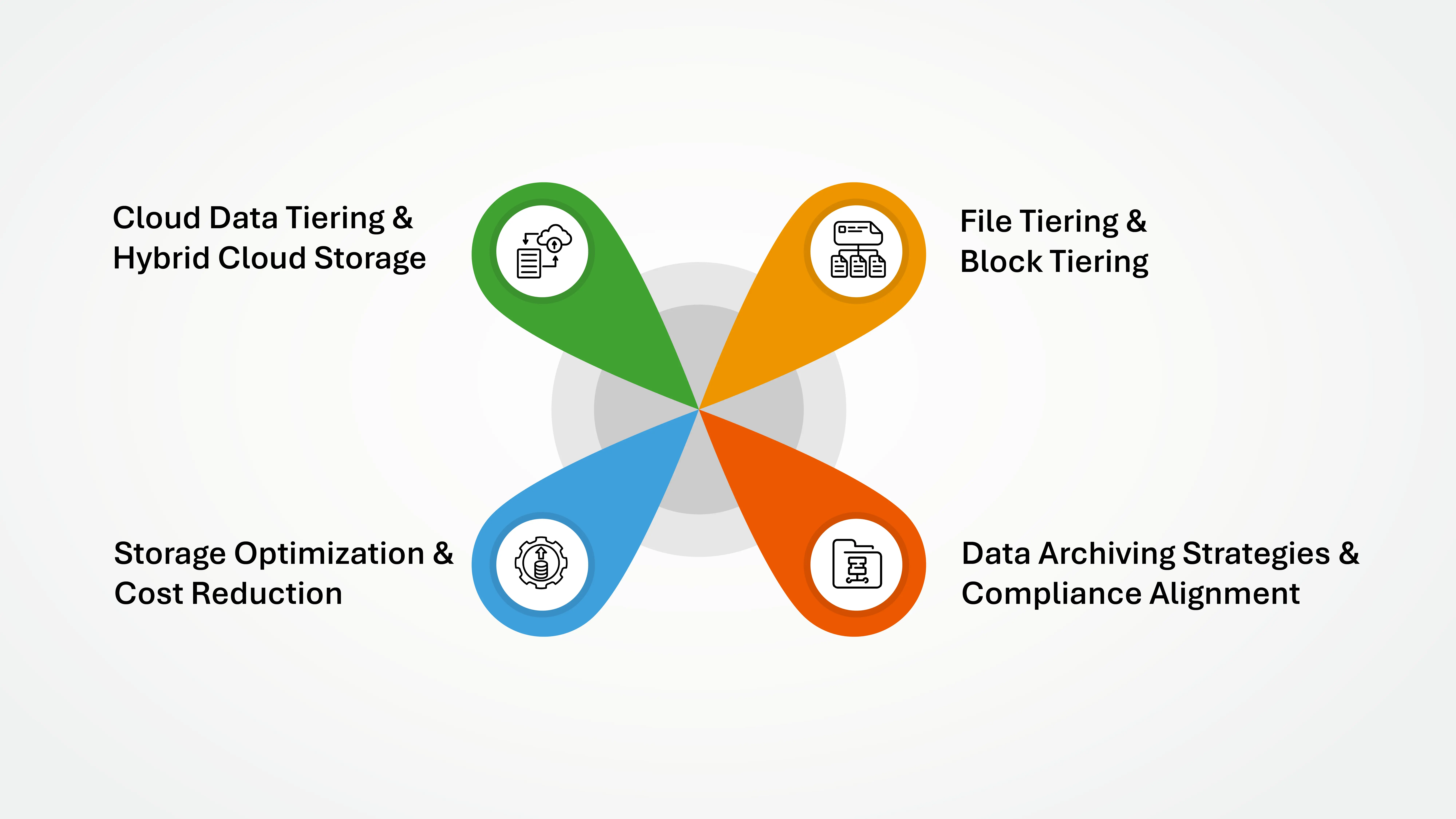
1. Cloud Data Tiering & Hybrid Cloud Storage
With businesses increasingly shifting to hybrid cloud storage, adopting cloud tiering solutions is essential for balancing performance, cost, and security. Cloud data tiering automates the movement of cold data to cost-effective cloud storage while keeping frequently accessed data on high-speed storage tiers. This approach enables:
- Seamless data migration between on-prem and cloud environments
- Optimized cloud storage costs with tiered pricing models
- Better scalability and improved data availability
2. File Tiering & Block Tiering
Organizations using structured and unstructured data benefit from file tiering and block tiering, which optimize storage performance by:
- File Tiering: Automatically moving inactive files from expensive storage to low-cost cloud or archival storage while maintaining accessibility.
- Block Tiering: Optimizing block storage by shifting rarely used data blocks to lower-cost storage tiers, reducing storage expenses without affecting performance.
Both techniques contribute to cost-effective data storage while ensuring business-critical data remains readily available when needed.
3. Data Archiving Strategies & Compliance Alignment
An effective data archiving strategy is essential for managing historical records, regulatory data, and rarely accessed information. By integrating data archiving solutions into tiered data storage, organizations can:
- Ensure compliance with GDPR, CCPA, and data sovereignty laws
- Enhance security by placing sensitive data in restricted storage tiers
- Reduce costs by moving infrequently accessed data to archival storage
4. Storage Optimization & Cost Reduction
By leveraging AI-driven data classification and storage optimization techniques, businesses can automate data movement across storage tiers, leading to:
- Significant storage cost reduction by using affordable cloud-based cold storage
- Enhanced performance by freeing up high-speed storage for active workloads
- Automated compliance monitoring for data retention policies
Best Practices for Cloud Data Tiering
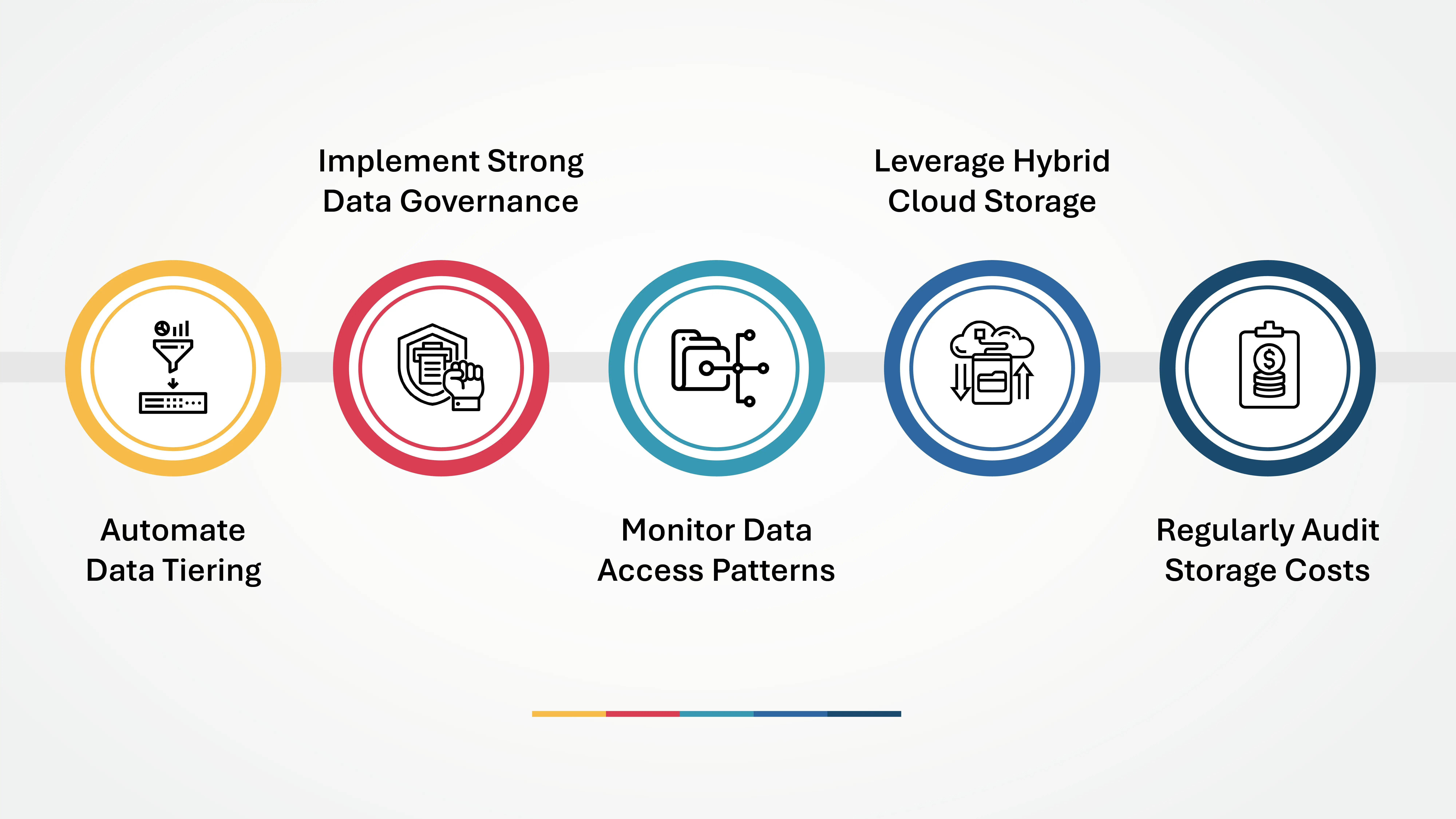
To maximize the benefits of data tiering in the cloud, organizations should follow these best practices for cloud data tiering:
- Automate Data Tiering: Use AI-driven intelligent data management solutions to classify and migrate data dynamically.
- Implement Strong Data Governance: Ensure data movement aligns with security, compliance, and business policies.
- Monitor Data Access Patterns: Regularly analyze data usage trends to optimize tiering strategies.
- Leverage Hybrid Cloud Storage: Use a mix of on-premises and cloud storage to balance performance, cost, and control.
- Regularly Audit Storage Costs: Continuously optimize storage utilization to prevent unnecessary cloud expenses.
The Future of Data Tiering
As AI-driven storage management and intelligent data governance continue to evolve, the future of data tiering will focus on greater automation, cost-efficient storage models, and compliance-driven data movement. Businesses that adopt automated cloud tiering solutions will gain:
- Real-time visibility into data usage and movement
- Optimized cloud storage utilization across hybrid environments
- Stronger compliance with evolving data protection laws
By implementing cloud data tiering, file tiering, block tiering, and automated data archiving solutions, enterprises can transform data tiering into a strategic advantage—enhancing efficiency, reducing costs, and ensuring data security in an ever-expanding digital landscape.
Getting Started with Data Dynamics:
- Read the latest blog: The CIO-CDO Partnership: Turning Data Chaos into AI-Driven Strategy
- Learn about our Unstructured Data Management Software – Zubin
- Schedule a demo with our team






