In an age where data is both an asset and a liability, data retention compliance is emerging as a critical checkpoint for enterprises. With the volume and types of data increasing by the second, businesses must navigate a complex web of legal regulations, regulatory requirements, and storage challenges—all while ensuring compliance with frameworks like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and other global data protection regulations. But what exactly is data retention compliance, and why does it matter more than ever today?
Let’s break it down.
What Is Data Retention Compliance?
Data retention compliance refers to the policies and practices an organization uses to manage how long it stores different types of data and when it deletes them—in line with applicable regulatory compliance mandates. These mandates define how long personal data, backup data, business documents, emails, financial records, and critical data must be securely stored, and when that data should be deleted.
Think of it as setting a retention schedule for every piece of data collected or processed, ensuring it is securely stored only for the appropriate amount of time, no longer. This practice is particularly crucial for publicly traded companies, financial institutions, healthcare providers, and any business handling sensitive or personal information.
Why Is Data Retention Compliance Important Today?
In today’s regulatory landscape, keeping data “just in case” is no longer a safe or affordable strategy. Here’s why:
- Legal exposure: Holding onto specific data beyond the retention period can violate legal regulations and increase exposure to lawsuits or fines under GDPR and other compliance frameworks.
- Privacy obligations: Regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) require organizations to delete data that is no longer necessary for its original purpose. Storing data for longer periods can put you at odds with data protection regulation.
- Storage costs: More data equals higher storage costs. A lack of clarity around data lifecycle management leads to the unnecessary storage of outdated or irrelevant data.
- Cyber risk: Holding on to data indefinitely increases the risk of data loss, breaches, and unauthorized data access, especially if it’s not securely stored.
- Operational efficiency: Knowing where your specific data resides and how long it should be retained can streamline operations and improve responsiveness during audits or legal holds.
Key Elements of Data Retention Compliance
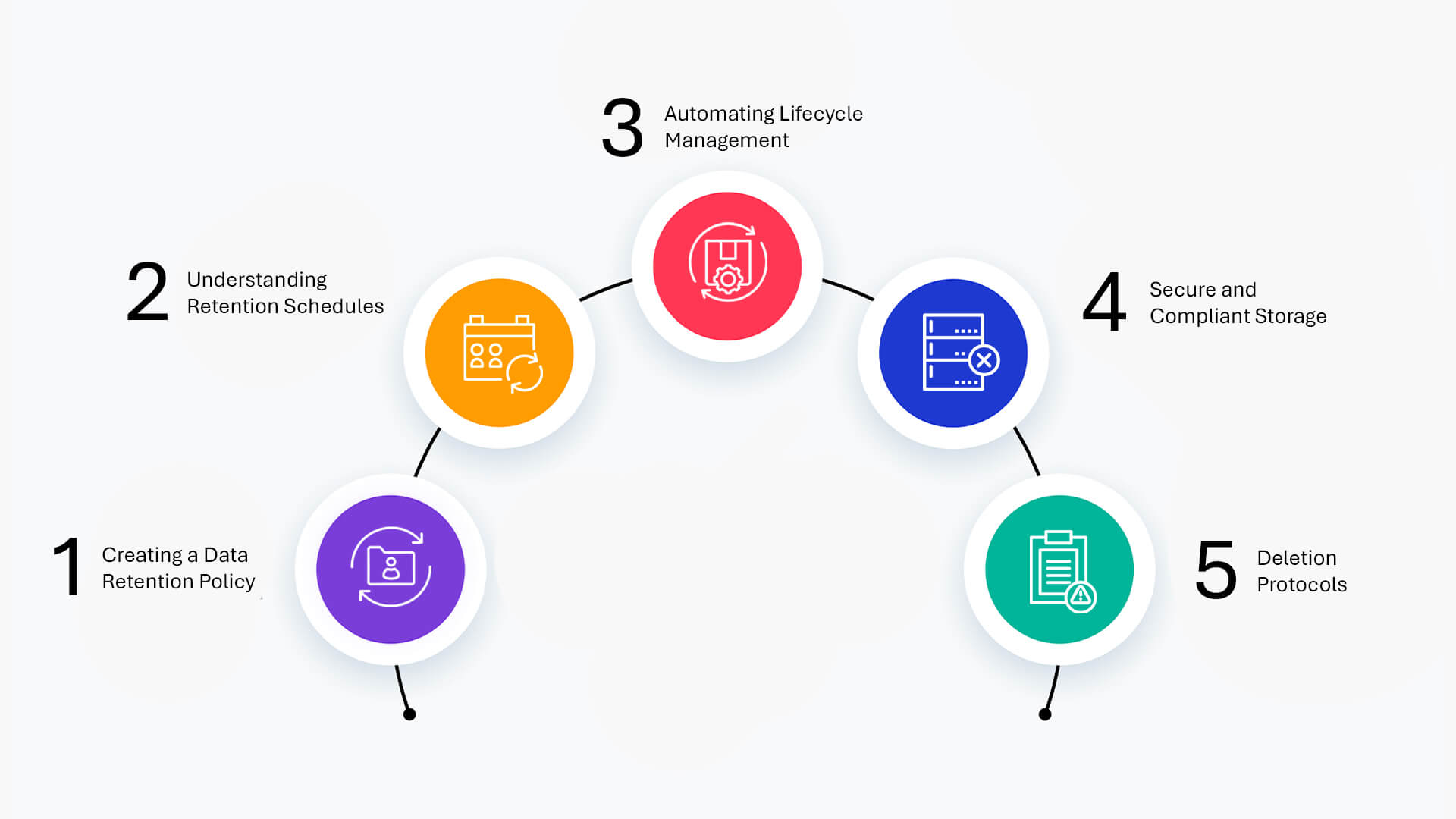

- Creating a Data Retention Policy: A strong data retention compliance program begins with a comprehensive data retention policy. This document should outline the types of data your organization collects, why it’s collected, how it’s stored, and how long it will be kept. This policy must align with the regulatory compliance obligations relevant to your industry and geography.
- Understanding Retention Schedules: Different types of data have different retention schedules. For example, financial records may need to be retained for 7 years in some jurisdictions, while personal data used for marketing might have a much shorter amount of time defined by GDPR. A retention schedule ensures timely deletion while allowing access to critical data when needed.
- Automating Lifecycle Management: Data lifecycle management tools can automatically enforce retention schedules, delete data when required, and archive information based on risk, value, or regulation. Automating this process helps organizations stay ahead of compliance requirements without manual intervention.
- Secure and Compliant Storage: Data must be securely stored across its lifecycle—from initial capture to final deletion. This includes managing backup data, monitoring data access, and using encryption to protect personal information and critical data.
- Deletion Protocols: A big part of compliance is knowing when to delete data. Whether it’s in response to a user’s right to be forgotten under the GDPR, or part of regular records retention clean-up, deletion must be done systematically and probably to ensure compliance and reduce risk.
Challenges and Considerations
Enterprises often face several hurdles in achieving data retention compliance, including:
- Fragmented data storage across on-prem, cloud, and hybrid systems.
- Lack of visibility into data collected, making it hard to apply retention policies uniformly.
- Compliance requirements that vary by region, industry, and data category.
- Difficulty in distinguishing personal data from general enterprise data.
- Risks of retaining specific data longer than legally allowed.
How Businesses Can Ensure Compliance
To prevent data breaches, fines, or inefficiencies, businesses must implement:
- Regular audits of data storage systems.
- Cross-functional coordination between legal, IT, and compliance teams.
- Clear training programs on regulatory requirements and best practices.
- Implementation of tools that support data lifecycle management with policy-based automation and visibility.
Getting Started with Data Dynamics:
- Learn about Unstructured Data Management
- Schedule a demo with our team
- Read the latest blog: From Burden to Breakthrough: How Data Governance Fuels AI, Trust, and Business Growth in 2025 and Beyond






