What is a Data Footprint?
A data footprint refers to the digital trail left by individuals, businesses, and devices through data creation, storage, sharing, and processing. This includes structured and unstructured data from sources like emails, enterprise databases, IoT devices, and AI-driven analytics. As data consumption skyrockets, optimizing the data footprint is crucial for business data management, data storage optimization, and data processing efficiency while maintaining strong data security and GDPR and CCPA compliance.
Why is Data Footprint Important?
As enterprises scale, their data footprint grows exponentially, posing challenges that impact security, compliance, and costs:
- Data breach prevention: A larger data footprint increases exposure to cyber threats, making data privacy compliance essential.
- Regulatory data storage: Compliance with data compliance regulations like GDPR and CCPA requires strict data governance frameworks to ensure proper handling of sensitive information.
- Reduced operational costs: Redundant data removal and optimized data architecture help prevent unnecessary storage expenses.
- Data processing performance: Effective data lifecycle management ensures real-time access to critical data management assets.
- Environmental impact: Data storage optimization reduces energy consumption in data centers, promoting sustainability.
By implementing strategic business data management and data governance policies, organizations can secure their data footprint while enhancing data processing efficiency.
Key Aspects of Data Footprint Management
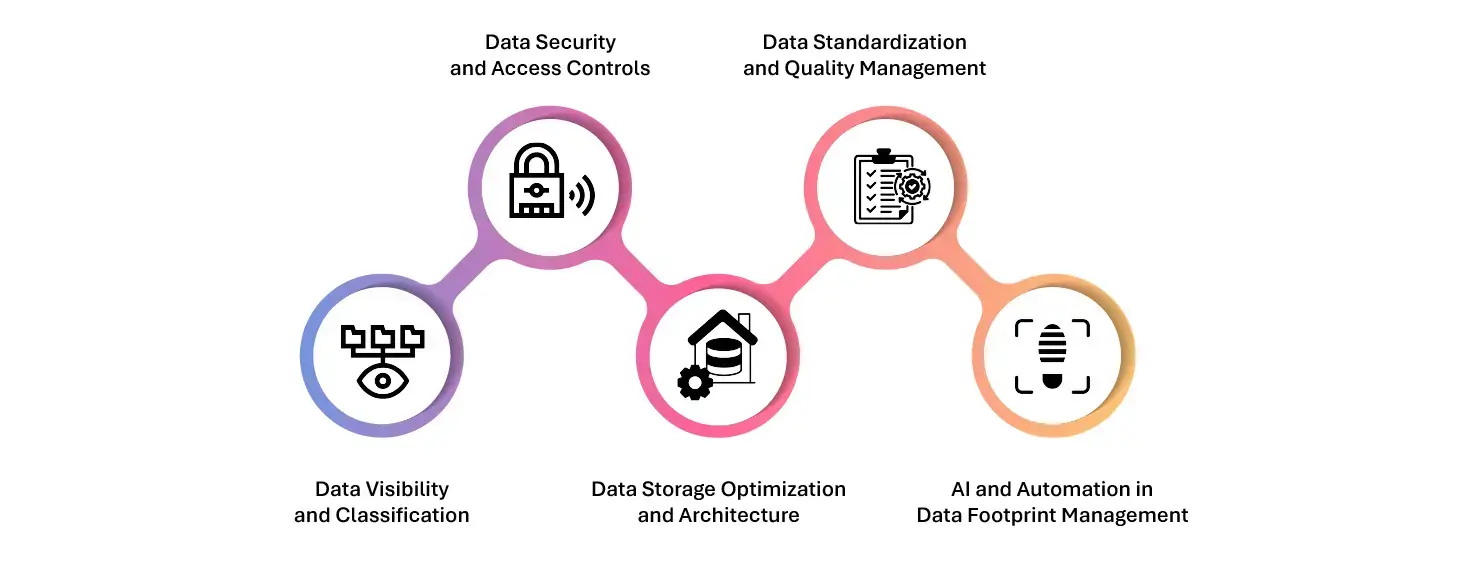

1. Data Visibility and Classification
- Data analytics enhancement helps organizations gain insights into structured and unstructured data, ensuring proper handling.
- Data classification frameworks support data governance, categorizing information based on sensitivity, retention policies, and access control.
- Data integrity monitoring safeguards critical data management and ensures compliance with data compliance regulations.
2. Data Security and Access Controls
- Data breach prevention mechanisms, such as data encryption, protect sensitive information.
- Zero Trust security models and role-based access control (RBAC) ensure secure data access across scalable data architectures.
- Data privacy compliance requires real-time monitoring of regulatory data storage to avoid unauthorized access.
3. Data Governance and Compliance
- Data governance frameworks define policies for data lifecycle management and retention schedules.
- GDPR and CCPA compliance mandates clear data usage policies and transparent reporting.
- Audit logs and traceability provide visibility into business data management practices.
4. Data Storage Optimization and Architecture
- Data storage optimization includes redundant data removal and compression techniques.
- Data lakehouse integration allows organizations to combine structured and unstructured data for improved data analytics enhancement.
- Scalable data architecture supports optimized data architecture, ensuring seamless scalability without overburdening resources.
5. AI and Automation in Data Footprint Management
- AI-driven analytics optimize data processing performance, identifying inefficiencies and security risks.
- Automated compliance monitoring ensures adherence to data compliance regulations.
- Self-service data management enhances productivity by streamlining data processing efficiency.
Industry Insights and Trends
- Every day, the world generates a staggering 402.74 million terabytes of data, fuelling the exponential growth of the digital universe.
- 68% of stored data remains unused, indicating inefficiencies in business data management.
- According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), global power consumption from data centers and cryptocurrency mining is projected to surge by 80% between 2022 and 2026. In the EU alone, data center energy usage could rise by 60% by 2030, underscoring the growing demand for sustainable energy solutions in the digital age.
Getting Started with Data Footprint Optimization
To take control of your organization’s data footprint, consider these steps:
✔ Implement data analytics enhancement tools to monitor structured and unstructured data effectively.
✔ Strengthen data security and data privacy compliance policies to ensure secure storage and access.
✔ Optimize data storage with redundant data removal and automated data lifecycle management strategies.
✔ Leverage AI-driven data processing performance tools to enhance business data management efficiency.
By proactively managing their data footprint, organizations can enhance security, reduce costs, ensure compliance, and drive sustainability through optimized data governance practices.
Getting Started with Data Dynamics:
- Read the latest blog: Clean Tech, Big Impact: Why Sustainable AI is the Next Big Thing for Future-Focused Businesses
- Learn about our Unstructured Data Management Software – Zubin
- Schedule a demo with our team






