What is a Data Breach?
A data breach refers to an incident where sensitive, confidential, or protected information is accessed, disclosed, or stolen by unauthorized individuals. These breaches can occur due to cyberattacks, insider threats, human errors, or system vulnerabilities. Organizations of all sizes and across industries are at risk, making data breaches a major concern for businesses, governments, and individuals alike.
How Do Data Breaches Happen?
Data breaches can occur in various ways, often exploiting weaknesses in an organization’s security framework. Some common causes include:
- Cyberattacks: Hackers use techniques like phishing, malware, ransomware, or brute-force attacks to infiltrate systems and steal data.
- Insider Threats: Employees or contractors with access to sensitive information may intentionally or unintentionally leak data.
- Weak Passwords & Credential Theft: Poor password hygiene, credential stuffing, and social engineering attacks make it easier for hackers to gain unauthorized access.
- Unpatched Software & System Vulnerabilities: Outdated software or unpatched security flaws create loopholes that attackers can exploit.
- Third-Party Breaches: Vendors, partners, or cloud service providers with weak security measures can become the weak link leading to data exposure.
- Physical Theft: Stolen laptops, USB drives, or even misplaced paper documents can lead to a data breach.
Types of Data Breaches
- Personal Data Breaches: Involves unauthorized access to personally identifiable information (PII) such as names, addresses, social security numbers, and financial details.
- Financial Data Breaches: Includes the exposure of banking information, credit card details, and financial transaction records.
- Healthcare Data Breaches: The unauthorized access or theft of medical records, patient history, and insurance details, violating HIPAA and other regulations.
- Intellectual Property Theft: Cybercriminals or competitors stealing trade secrets, proprietary research, and confidential business strategies.
- Government & Military Breaches: Exposure of classified information, national security data, or intelligence leaks.
Impact of a Data Breach
The consequences of a data breach can be severe, affecting both individuals and organizations. Some of the key impacts include:
- Financial Loss: Companies face regulatory fines, legal fees, ransom payments, and revenue loss.
- Reputational Damage: A breach erodes consumer trust and can lead to customer attrition.
- Regulatory Penalties: Governments impose hefty fines under laws such as GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA, and PCI DSS.
- Operational Disruptions: Businesses may suffer downtime, data loss, and productivity setbacks.
- Identity Theft & Fraud: Breached personal data can be used for identity theft, fraud, and black-market sales.
How to Prevent Data Breaches
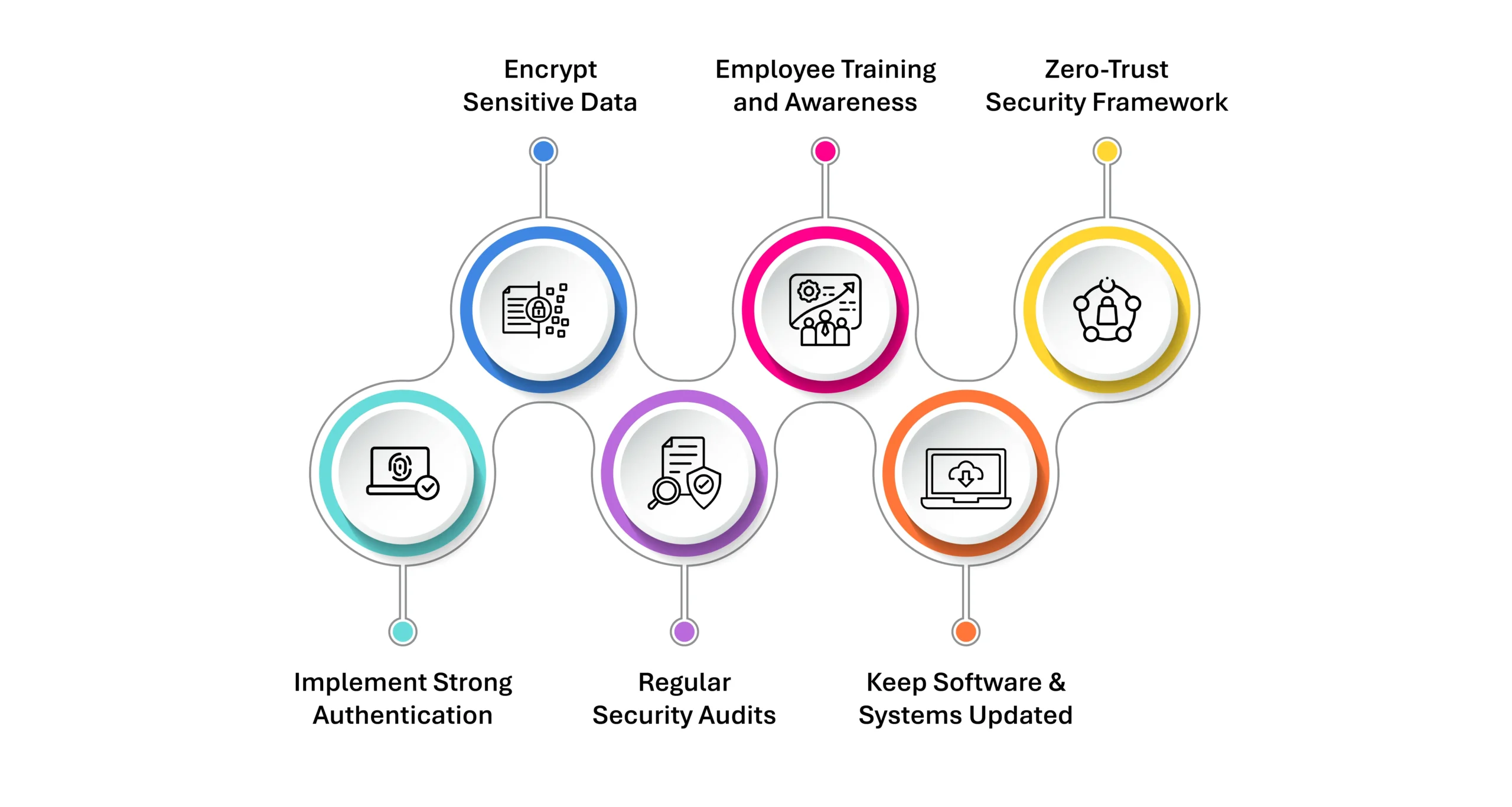
Organizations and individuals can take proactive measures to prevent data breaches, including:
- Implement Strong Authentication: Use multi-factor authentication (MFA) and strong passwords to prevent unauthorized access.
- Encrypt Sensitive Data: Encryption ensures that even if data is stolen, it remains unreadable without decryption keys.
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct vulnerability assessments and penetration testing to identify security gaps.
- Employee Training & Awareness: Educate employees on phishing, social engineering, and safe cybersecurity practices.
- Keep Software & Systems Updated: Regularly patch vulnerabilities in applications and operating systems.
- Zero-Trust Security Framework: Restrict access to only those who need it and continuously verify trust before granting permissions.
- Incident Response Plan: Have a robust response plan in place to detect, contain, and mitigate breaches quickly.
Data breaches continue to rise, driven by increasingly sophisticated cyber threats and human vulnerabilities. Organizations must take a proactive approach to data security, implementing robust cybersecurity measures, compliance frameworks, and employee training to minimize risks. In today’s digital world, protecting sensitive data is not just a security measure—it is a fundamental business imperative.
Getting Started with Data Dynamics:
- Learn about Unstructured Data Management
- Schedule a demo with our team
- Read the latest blog: The New Frontier in Data Security: Rethinking Privacy and Compliance in 2025 and Beyond






