What is Unstructured Data Storage?
Unstructured data storage refers to the storage systems and technologies used to store, manage, and retrieve data that does not have a predefined schema or easily searchable structure. Unlike structured data, which is neatly organized in relational databases with rows and columns, unstructured data includes files, images, videos, emails, documents, logs, IoT sensor data, and more—often growing exponentially.
Since the volume, variety, and velocity of unstructured data cannot be accommodated in traditional storage architectures, companies require intelligent, scalable, and metadata-driven storage today. The exponential growth rate of unstructured data makes organizations seek storage that preserves the information, optimizes, secures, and offers real-time access.
Types of Unstructured Data Storage: What Works for Your Business
Unstructured data is varied, and so are the storage solutions designed to handle it. Whether it is massive multimedia files, logs, sensor data, or AI-generated insights, enterprises need storage architectures that balance performance, scalability, accessibility, and cost efficiency. Unlike structured data, which fits neatly into relational databases, unstructured data requires specialized storage models that allow flexible, high-volume management across on-premises, cloud, and hybrid environments.
It’s time for more technical detail. Here’s an overview of the key types of unstructured data storage.
Object Storage
Object storage is the backbone of cloud-native data management. Designed for scale and distributed access, it replaces traditional hierarchical structures with rigid folder definitions, storing each file as an object with metadata that makes it searchable and retrievable across global environments. Platforms such as AWS S3, Azure Blob, and Google Cloud Storage, in its end, utilize object storage for large datasets: their models for artificial intelligence training to media libraries. Its redundancies and scalability make it a go-to choice for unlimited capacity without the complication of traditional storage.
File Storage (NAS – Network Attached Storage)
NAS is ideal for team collaboration and shared access since its file storage follows a structured, hierarchical format. The use of this NAS might prove useful for an enterprise that deals with large volumes of documents, media files, or research reports and is familiar with a directory-based structure that allows for role-based permissions and enterprise integration. Be it a law firm managing case files, a media house working through high-resolution videos, or a corporate team accessing shared reports, NAS solutions take care of easy, yet controlled, data sharing across departments.
Block Storage
Block storage is optimized for performance and speed, breaking data into fixed-size chunks (“blocks”) and storing them separately. It is best suited for high-speed transactional systems, including financial trading, AI model inferencing, and real-time analytics. Since applications interact with data at the block level rather than as whole files, this approach is critical for databases, virtual machines, and latency-sensitive workloads where milliseconds matter.
Data Lakes
A store-now, analyze-later approach, data lakes allow businesses to dump massive volumes of unstructured and semi-structured data into a scalable, flexible environment, unlike traditional storage, which requires predefined schemas for storage. Business ingests raw data and processes only when necessary. They are very essential for all AI, machine learning, and big data analytics activities where large datasets drive insights. They track customer behavior by retailers, risk models for financial institutions, and storage and analysis of patient data for medical research by healthcare providers.
Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Storage
Blending on-prem security with the scalability of cloud, hybrid, and multi-cloud storage ensures balanced compliance, efficiency, and adaptability. Organizations that need data sovereignty and observe regulatory limitations might want to use on-prem for sensitive information while allowing others to store natively in a cloud for not-so-sensitive workload requirements. These are more practical in finance and healthcare organizations along with large firms operating globally when data is generated in various geographical locations and needs to be fetched from time to time by these AI, Analytics, and Operation systems.
Key Characteristics of Unstructured Data Storage
Modern unstructured data storage is not merely a matter of where the data sits, but its scalability, efficiency, and security ensure that data is accessible, optimized, and protected. The following is a summary of what makes unstructured data storage a critical part of enterprise infrastructure today:
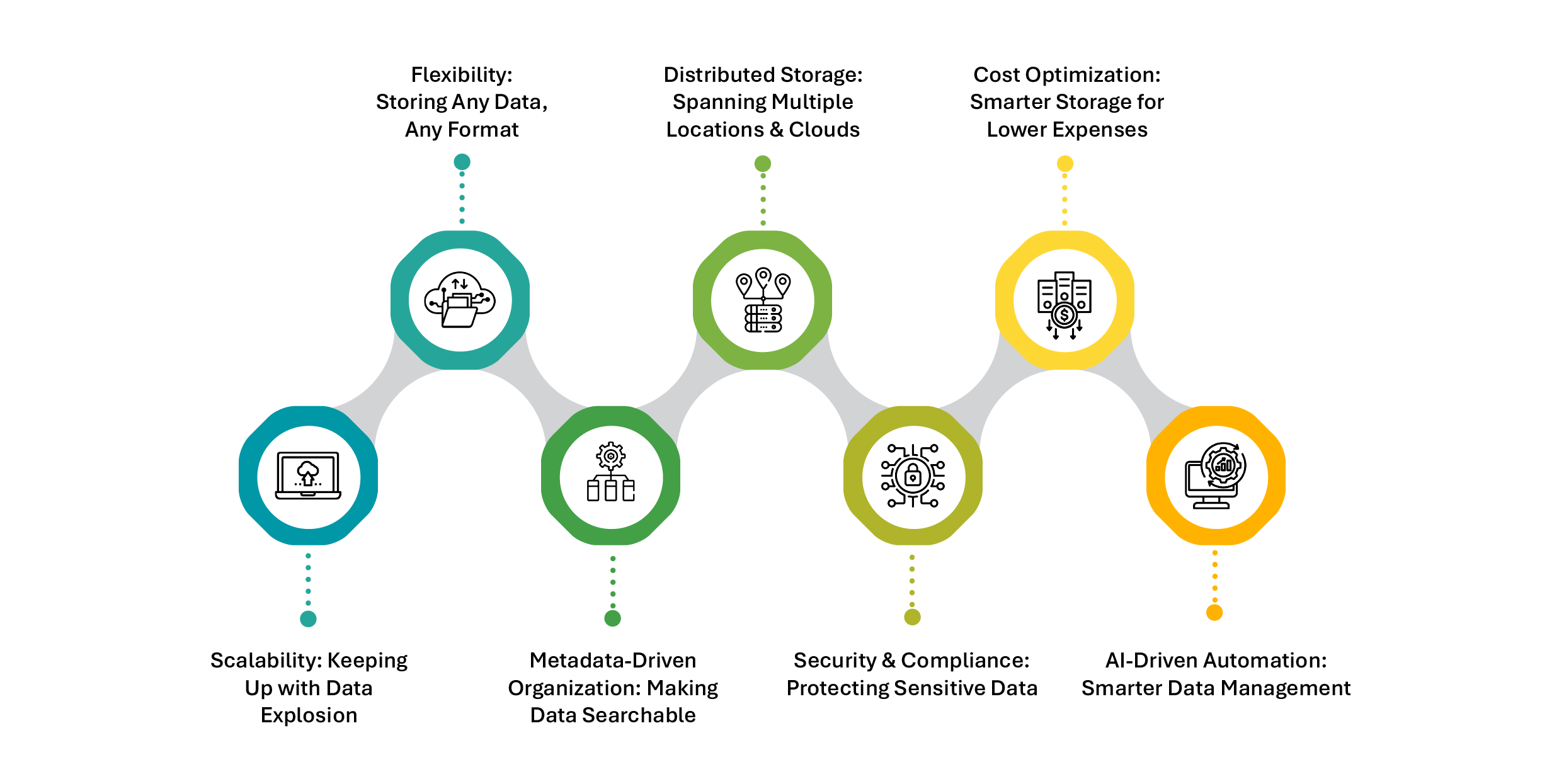

Scalability: Keeping Up with Data Explosion
Unstructured data is growing at an exponential rate, and businesses need storage that scales with demand. Traditional storage infrastructures cannot keep up, causing performance bottlenecks, costs that spiral out of control, and operational inefficiencies. Scalable storage solutions—such as cloud-based object storage and distributed architectures—enable organizations to handle exponential data growth without disruption.
Flexibility: Storing Any Data, Any Format
Enterprises produce data in various forms: text, images, videos, logs, and machine-generated files. Each of these has different storage requirements. A strict storage structure cannot be applied here. Flexible storage solutions support a variety of data types without forcing them into predefined schemas.
Metadata-Driven Organization: Making Data Searchable
Unstructured data often lacks organization, making search and retrieval difficult. Metadata tagging and AI-driven indexing solve this challenge, ensuring businesses can quickly find and act on the right data.
Distributed Storage: Spanning Multiple Locations and Clouds
Data isn’t confined to one place anymore. Businesses operate in hybrid and multi-cloud environments, meaning unstructured data is stored across on-premises data centers, private clouds, and public cloud providers. A distributed storage model ensures seamless data access while reducing compliance risks and storage costs.
Security and Compliance: Protecting Sensitive Data
Often containing confidential business intelligence, personally identifiable information, or trade secrets, unstructured data calls for utmost secure storage and risk management against potential breaches and related regulatory fines as well as reputational damages. Secure solutions will include such key features as encryption, access controls, and automated compliance monitoring.
Cost Optimization: Smarter Storage for Lower Expenses
Storing unstructured data can be expensive; however, not all data needs high-performance storage. Intelligent tiering and archiving strategies make sure that active data remains in high-speed storage, while the inactive data gets moved to the lower-cost archival storage.
AI-Driven Automation: Smarter Data Management
Managing massive amounts of unstructured data manually is impossible. AI-driven storage solutions automate data classification, anomaly detection, and policy enforcement, thus reducing human effort while improving efficiency.
Storage for unstructured data is no longer just about how much information it can hold but about its accessibility, scalability, and security in a world where data truly rules.
Leaning on the intelligent, metadata-driven, AI-powered storage solution will help a business transform this challenge into a strategic asset.
Industry Insights and Trends
- Unstructured data is increasing at an annual rate of 55–65%, which gives a sense of the growing imperative for effective storage solutions.
- The global data storage market is likely to grow from $218.33 billion in 2024 to $774.00 billion by 2032, indicating a compound annual growth rate of 17.1%.
- Artful domination of AI and deep learning into data systems is the largest transformation occurring in technological infrastructure. Current data storage systems challenge the frequent need of access to a large amount of information by AI, leading to unified resilient storage solutions.
Getting Started with Data Dynamics:
- Learn about Unstructured Data Management
- Schedule a demo with our team
- Read the latest blog: Data Fabric and AI: The Blueprint for Dominating Unstructured Data in 2025