What is Data Control?
Data control refers to the strategic processes, policies, and technologies that regulate data access control, security, and governance within an organization. As enterprises continue to generate massive volumes of data, ensuring data security, data privacy, and data protection is crucial for safeguarding personal data and preventing unauthorized access to sensitive information.
Effective data control helps organizations balance accessibility with security, ensuring that sensitive data is only available to authorized users while maintaining data integrity and compliance with regulatory frameworks. Without robust data protection measures, businesses risk exposure to cyber threats, operational inefficiencies, and regulatory penalties.
Why is Data Control Important?
In an era of increasing data-driven decision-making, maintaining stringent data security control is non-negotiable. Organizations that lack proper data management frameworks often struggle with security breaches, compliance violations, and inefficient data usage.
Key challenges include:
- Unauthorized data access control leading to breaches of personal data.
- Poor data governance resulting in regulatory non-compliance.
- Lack of visibility into sensitive information, increasing risks of data exposure.
- Inefficient data protection measures, causing operational inefficiencies.
By implementing strong data security policies and leveraging AI-driven automation, businesses can establish proactive data management strategies that secure their sensitive data while ensuring accessibility for authorized stakeholders.
Key Aspects of Data Control
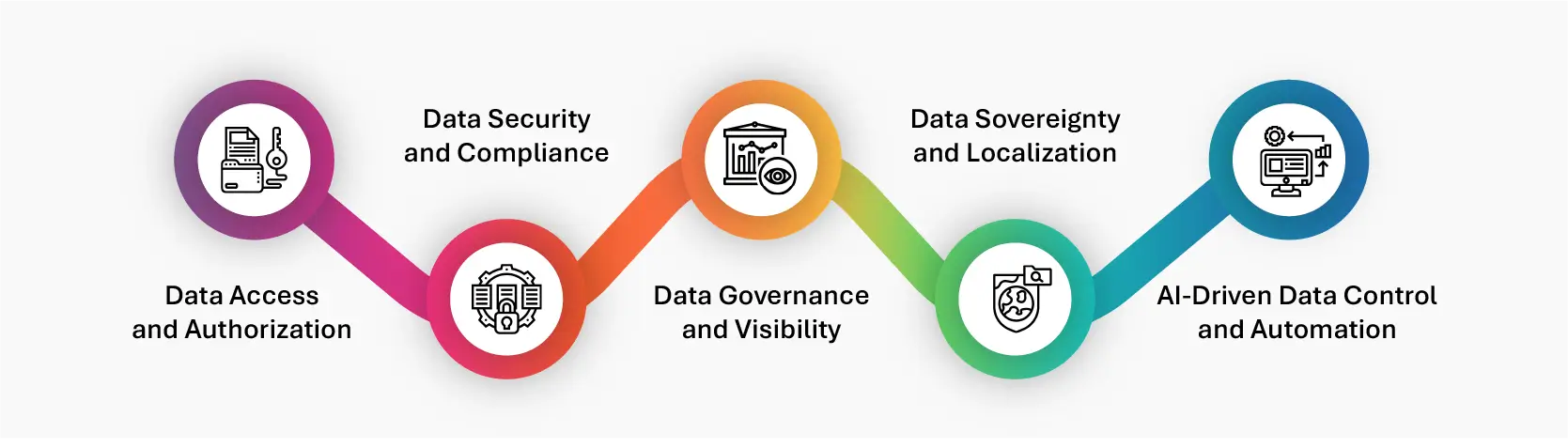

1. Data Access and Authorization
- Organizations must enforce strict data access control mechanisms such as Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) and Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC) to regulate who can access sensitive information.
- Zero Trust Security Models ensure that all access requests are continuously verified, enhancing data security control.
- Implementing data encrypted protocols protects personal data from unauthorized interception.
2. Data Security and Compliance
- Data protection measures such as encryption and tokenization ensure that sensitive data remains secure in transit and at rest.
- Compliance with industry standards like GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA, and the DPDP Act helps organizations avoid legal penalties and strengthen data privacy.
- Automated data security control solutions detect and mitigate cyber threats in real time, ensuring robust data integrity.
3. Data Governance and Visibility
- Establishing a data governance framework enables enterprises to classify and manage sensitive information based on security levels and access rights.
- Data classification and tagging improve data management by ensuring that data is stored, accessed, and processed securely.
- Audit logs and traceability provide insights into data usage, strengthening data privacy compliance.
4. Data Sovereignty and Localization
- Global data security regulations mandate that sensitive data be stored within specific geographic regions. Organizations must implement data protection measures to comply with these laws.
- Hybrid and multi-cloud data management strategies help balance accessibility while adhering to localization requirements.
5. AI-Driven Data Control and Automation
- AI-powered analytics enhance data governance by monitoring data access control patterns and identifying anomalies.
- Automated data security control ensures that compliance policies are enforced without manual intervention.
- Self-service data management empowers employees to access and use sensitive information securely while reducing IT dependency.
Industry Insights and Trends
- According to IBM’s 2024 Cost of a Data Breach Report, the global average cost of a data breach reached $4.88 million in 2024, highlighting the financial impact of inadequate data control measures.
- 68% of data available to businesses goes unleveraged, indicating challenges in making collected data usable and managing storage effectively.
- A staggering 96% of organizations acknowledge an ethical obligation to handle data responsibly. However, their approach to earning and maintaining customer trust does not always align with consumer expectations. Transparency—offering clear, easily accessible information on how data is used—emerged as the top consumer priority (39%), ranking well above concerns such as preventing the sale of personal information or mere compliance with privacy regulations.
Getting Started with Data Control
To establish a secure and compliant data management ecosystem, organizations should:
✔ Implement data security control frameworks with automated access management.
✔ Leverage AI to enhance data protection and compliance monitoring.
✔ Ensure data integrity through classification, governance, and encryption.
✔ Adopt data access control solutions that balance security with accessibility.
Strong data control practices not only safeguard sensitive data but also drive operational efficiency and regulatory compliance. By integrating AI-driven automation, data governance policies, and secure data access control, organizations can transform data management into a strategic advantage.
Getting Started with Data Dynamics:
- Read the latest blog: From Burden to Breakthrough: How Data Governance Fuels AI, Trust, and Business Growth in 2025 and Beyond
- Learn about our Unstructured Data Management Software – Zubin
- Schedule a demo with our team