What are Data Privacy Regulations?
Data privacy regulations are legal frameworks that govern how personal data is collected, processed, stored, shared, and protected. They establish guidelines to ensure individuals have control over their personal information while holding organizations accountable for responsible data handling. These laws aim to prevent unauthorized access, misuse, and breaches, promoting transparency, security, and ethical data practices across industries.
Data privacy regulations vary globally, addressing different aspects of personal data protection based on regional priorities and industry needs. Broadly, they can be classified into comprehensive, sector-specific, regional, and consumer-centric regulations. Comprehensive regulations apply across industries and provide overarching data protection frameworks, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the EU and Brazil’s General Data Protection Law (LGPD), both of which emphasize consent, transparency, and accountability. Sector-specific regulations focus on industry-specific data protection, ensuring compliance with stringent security and privacy requirements. Examples include the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the US for healthcare data, the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA) for financial institutions, and the Children’s Online Privacy Protection Act (COPPA) for protecting children’s personal information collected online.
In contrast, regional or national regulations are country-specific laws that prioritize data sovereignty and localization, restricting how personal data is stored and transferred across borders. For example, China’s Personal Information Protection Law (PIPL) imposes strict cross-border data transfer restrictions, while India’s Digital Personal Data Protection Act (DPDP Act) sets compliance norms for companies handling Indian citizens’ data. Meanwhile, consumer-centric privacy laws focus on empowering individuals with greater control over their data, particularly in digital economies. The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) grants California residents rights to access, delete, or opt out of data collection, while the Virginia Consumer Data Protection Act (VCDPA) introduces GDPR-like privacy rights tailored for Virginia residents. These varying regulatory frameworks reflect the growing importance of data protection in a world increasingly reliant on digital information.
Key Aspects of Data Privacy Regulations
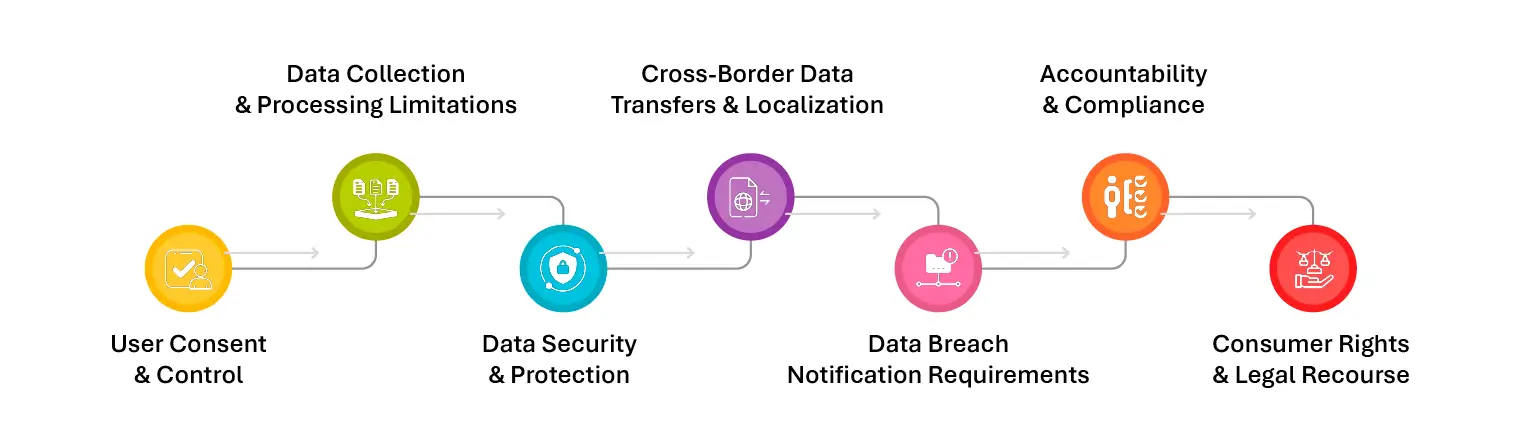
- User Consent & Control: Individuals must be informed about data collection practices and provide explicit consent before their data is processed. Regulations grant users the right to access, modify, delete, or transfer their personal information. Many laws mandate opt-in or opt-out mechanisms for data processing, marketing, and third-party data sharing.
- Data Collection & Processing Limitations: Regulations enforce data minimization, requiring organizations to collect only the necessary data for a specific purpose. Data processing must be lawful, fair, and transparent, ensuring organizations do not misuse personal information. Purpose limitations dictate that data should only be used for the declared and legitimate purpose for which it was collected.
- Data Security & Protection: Organizations must implement strong security measures such as encryption, anonymization, and access controls to protect personal information. Regular security audits and risk assessments are required to identify vulnerabilities and mitigate threats. Companies should also have an incident response plan in place to act swiftly in the event of a data breach.
- Cross-Border Data Transfers & Localization: Some regulations impose restrictions on data storage and transfer, requiring certain data to remain within national borders. Laws like GDPR allow cross-border data transfers only if appropriate safeguards, such as Standard Contractual Clauses (SCCs), are in place. Companies must ensure compliance with international security and privacy standards when moving data across jurisdictions.
- Data Breach Notification Requirements: Organizations must promptly report data breaches to regulatory authorities and affected individuals. GDPR mandates breach notification within 72 hours, while CCPA requires immediate disclosure for breaches affecting consumers. Transparency in handling security incidents is a key compliance requirement to maintain trust and accountability.
- Accountability & Compliance: Businesses must maintain records of their data processing activities and demonstrate compliance with applicable privacy laws. Some regulations require the appointment of a Data Protection Officer (DPO) to oversee compliance efforts. Non-compliance can result in financial penalties, legal action, and reputational damage.
- Consumer Rights & Legal Recourse: Individuals have legal avenues to file complaints or lawsuits against companies that mishandle their data. Regulations like CCPA allow users to opt out of data sales, while GDPR grants the “Right to be Forgotten,” enabling individuals to request data deletion. Regulatory bodies have the authority to enforce penalties, ensuring companies remain accountable for data privacy violations.
Why do Data Privacy Regulations Matter?
In an era where data fuels economies, decision-making, and technological advancements, data privacy regulations are the foundation of digital trust. Without them, businesses would have unchecked power over personal data, leading to widespread misuse, security breaches, and loss of consumer confidence. These regulations establish clear boundaries, ensuring that organizations collect, process, and store data responsibly while giving individuals control over their personal information. By enforcing accountability, they compel businesses to prioritize security, implement risk mitigation strategies, and build transparency into their operations. This is particularly crucial in industries like healthcare, finance, and artificial intelligence, where sensitive data drives innovation but also poses ethical and security risks. The ability to manage and protect data effectively is not just a compliance requirement—it is a competitive differentiator in today’s digital economy. Organizations that embrace privacy-first strategies are not only safeguarding their operations from regulatory fines and reputational damage but are also strengthening customer relationships and brand credibility.
Beyond compliance, data privacy regulations are shaping the future of AI governance, cross-border trade, and digital sovereignty. As AI models and machine learning algorithms increasingly rely on vast amounts of unstructured data, privacy laws ensure that data is ethically sourced, bias-free, and processed securely. They also enable a structured approach to data governance, balancing national security concerns with global data flows. For businesses operating in multiple jurisdictions, compliance with frameworks like GDPR, PIPL, and DPDP Act ensures seamless operations while mitigating legal risks. Governments, too, are leveraging data privacy laws to assert digital sovereignty, ensuring that critical national data remains within their control. As digital transformation accelerates, the ability to align business objectives with robust data privacy frameworks will define the leaders of tomorrow—those who not only comply with regulations but also leverage them as a catalyst for innovation, trust, and long-term resilience.
Getting Started with Data Dynamics:
- Read the latest blog: From Compliance to Competitive Edge: Why Data Sovereignty Is the New Business Imperative
- Learn about our Unstructured Data Management Software – Zubin
- Schedule a demo with our team






