What is Data Security & Governance?
Data security and governance are two interconnected disciplines that ensure the integrity, confidentiality, and compliance of data within an organization. Data security governance framework focuses on protecting data from unauthorized access, security breaches, and cyber threats, while data governance refers to establishing policies, procedures, and frameworks necessary for responsible data management. Together, they form the foundation of a trustworthy digital ecosystem where sensitive data is secure, compliant, and used ethically.
Why is Data Security & Governance Important?
In today’s big data-driven world, organizations generate, store, and process vast amounts of sensitive information. Without proper data governance management strategies and robust data security frameworks, data becomes vulnerable to security risks, misuse, and regulatory requirements non-compliance. The rise of sophisticated cyber threats, stringent global regulations, and increasing consumer concerns about privacy make it imperative for businesses to adopt effective data governance solutions.
Organizations that fail to implement these measures risk reputational damage, financial losses, and legal penalties. On the other hand, businesses that prioritize data security & governance gain a competitive advantage by building trust with customers, partners, and regulatory bodies.
Key Components of Data Security & Governance
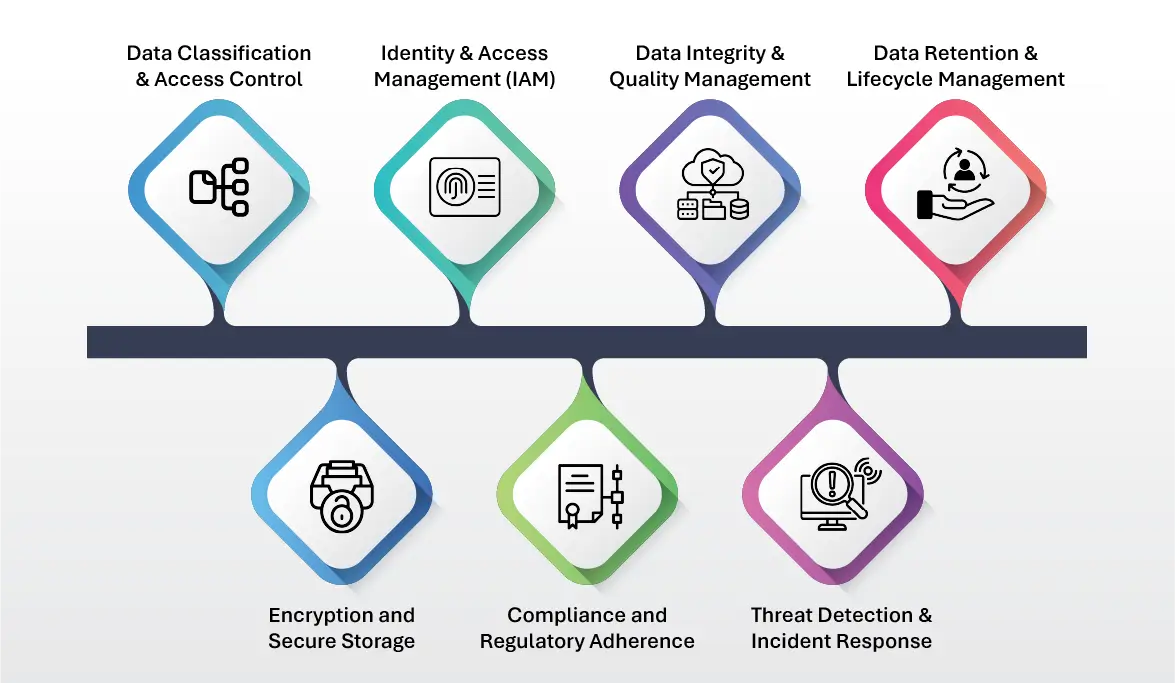
- Data Classification & Access Control: Organizations must implement data classification based on sensitivity levels and apply appropriate based access controls. Role-based access controls (RBAC) ensure that only authorized personnel can access specific data, reducing the risk of insider threats and unauthorized modifications.
- Encryption & Secure Storage: Data encryption is crucial for safeguarding data at rest, in transit, and in use. Encrypting sensitive data ensures that even if unauthorized parties gain access, the information remains unreadable and protected from misuse.
- Identity & Access Management (IAM): IAM frameworks help verify and control user access through multi-factor authentication (MFA), single sign-on (SSO), and privilege management. These measures strengthen data security governance while maintaining a seamless user experience.
- Compliance & Regulatory Adherence: Organizations must ensure compliance with regulations such as GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA, and industry-specific requirements. A well-defined governance structure ensures adherence to legal frameworks, minimizing the risk of penalties and enhancing data governance security and compliance.
- Data Integrity & Quality Management: Maintaining robust data governance is essential for accurate decision-making. Data stewards oversee data discovery, validation, audit trails, and quality checks to maintain consistency, reliability, and accuracy in big data environments.
- Threat Detection & Incident Response: AI-driven anomaly detection, real-time monitoring, and automated incident response help organizations proactively identify and mitigate security risks. A structured incident response plan minimizes the impact of security breaches and reduces downtime.
- Data Retention & Lifecycle Management: An effective data governance strategy defines data retention periods, archival procedures, and secure disposal methods. Organizations must manage the entire data lifecycle to reduce storage costs and ensure compliance with data governance solutions.
The Future of Data Security & Governance
The landscape of data security and governance is undergoing a seismic shift. As cyber threats grow more sophisticated and regulatory requirements become more stringent, traditional governance models are proving inadequate. The future lies in AI-driven security, zero-trust frameworks, and self-service governance, creating an ecosystem where data stewards play a more active role in risk management and compliance enforcement.
AI and automation are leading this transformation, enabling real-time threat detection, policy enforcement, and proactive security measures. Rather than relying on reactive strategies, businesses are moving toward predictive and autonomous governance models, where big data analytics and AI continuously analyze patterns, detect anomalies, and mitigate security risks before breaches occur.
At the same time, decentralized data governance management is gaining traction. Organizations are adopting self-service data governance solutions, empowering business units to take ownership of data classification, access controls, and regulatory compliance. This shift not only improves agility but also aligns with modern zero-trust architectures, ensuring robust data security without compromising operational efficiency.
The future of data security governance will be defined by adaptive compliance frameworks, AI-powered risk analysis, and federated governance structures that safeguard sensitive data while enabling seamless data access. Organizations that embrace these innovations will not only comply with evolving regulations but also gain a competitive advantage in securing their digital assets.
Getting Started with Data Dynamics:
- Read the latest blog: Unstructured Data: The Blind Spot CISOs and CIOs Must Solve—Together
- Learn about our Unstructured Data Management Software – Zubin
- Schedule a demo with our team






