In today’s data economy, privacy is more than just a regulatory requirement—it’s a fundamental necessity. Every online transaction, app usage, and digital interaction generates personal data that must be secured against misuse. With increasing data protection laws like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), businesses must prioritize data privacy in cybersecurity to prevent data breaches, protect sensitive information, and build consumer trust.
However, laws and regulations alone aren’t enough. Organizations must adopt a proactive data privacy framework, leveraging modern security tools, data loss prevention techniques, and stringent access controls to comply with regulatory compliance mandates and secure sensitive data.
What is Data Privacy?
Data privacy refers to the practice of handling and protecting personal and sensitive information to prevent unauthorized access, misuse, or breaches. It ensures that individuals have control over their data, determining how it is collected, stored, shared, and used.
Why Data Privacy Matters More Than Ever:
1. Explosion of Data Generation
From AI-powered applications to IoT devices, the sheer volume of consumer data being generated is unprecedented. Without effective data management, businesses struggle to track and protect sensitive information spread across multiple systems.
2. Regulatory Compliance is Tightening
Governments worldwide are enforcing strict data protection laws like the GDPR, CCPA, and India’s DPDP Act, mandating transparent data handling. Failure to meet regulatory requirements can lead to severe penalties, reputational damage, and operational disruptions.
3. Consumers Expect More Control Over Their Data
A study found that 87% of consumers consider data privacy a fundamental right. They demand better transparency, control, and security when sharing their personal data with companies.
4. The Rise of Cyber Threats
Cybercriminals are increasingly targeting sensitive data through ransomware, phishing, and insider threats. Without robust data loss prevention strategies, organizations risk costly data breaches that can compromise financial stability and customer loyalty.
Key Challenges in Data Privacy
1. Lack of Visibility and Control
Unstructured sensitive information scattered across hybrid and multi-cloud environments makes it difficult to monitor, classify, and secure data effectively.
2. Complexity of Regulatory Compliance
Different laws and regulations apply across various regions, creating data compliance challenges for global enterprises. A strong data privacy framework is essential for aligning with regulatory requirements and ensuring cross-border data security.
3. Balancing Innovation with Security
AI and data-driven technologies fuel innovation but also require responsible data usage. Companies must ensure data privacy in cybersecurity while leveraging consumer data for analytics and personalization.
4. Insider Threats and Third-Party Risks
Misconfigured access controls, employee negligence, and external vendors can expose sensitive data to unauthorized access, emphasizing the need for advanced security tools and monitoring mechanisms.
The Future of Data Privacy: Emerging Trends
1. Privacy-Enhancing Technologies (PETs): Advanced encryption methods, data loss prevention techniques, and anonymization tools are being deployed to secure personal data while enabling analytics.
2. AI-Powered Data Governance: Machine learning automates data management, preventing data breaches by detecting anomalies and enforcing data protection laws in real time.
3. Zero-Trust Security Models: Organizations are adopting a zero-trust approach, implementing stricter access controls and multi-factor authentication to prevent unauthorized data access.
4. Self-Service Data Privacy Frameworks: Consumers and employees are gaining more control over their sensitive information, allowing for consent-based data sharing in compliance with regulatory compliance requirements.
Best Practices for Strengthening Data Privacy
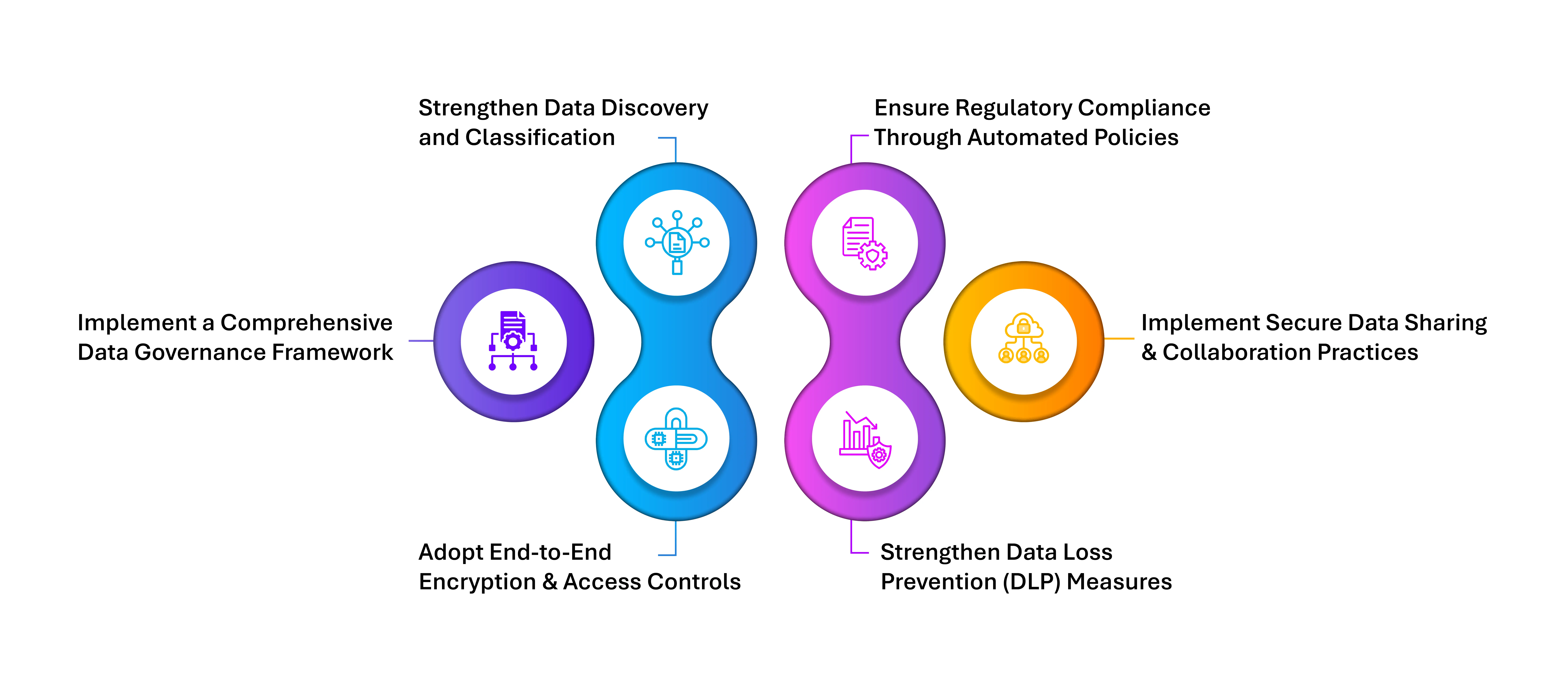

To build a resilient data privacy strategy, enterprises must take a proactive approach that integrates data governance, security, and compliance into everyday operations. Here are key best practices that enterprises can implement:
1. Implement a Comprehensive Data Governance Framework
A structured data governance strategy ensures that sensitive information is properly classified, stored, and protected. This includes:
- Defining clear data ownership roles for accountability.
- Establishing data classification policies to differentiate between public, confidential, and restricted data.
- Implementing data retention and disposal policies to prevent unnecessary exposure.
2. Strengthen Data Discovery and Classification
Data sprawl across hybrid and multi-cloud environments makes it challenging to locate, manage, and secure sensitive information. Automated data discovery and data classification help organizations:
- Identify high-risk and regulated data across distributed environments.
- Enforce data access policies based on sensitivity levels.
- Improve data visibility and control over structured and unstructured data.
3. Adopt End-to-End Encryption and Access Controls
Data encryption at rest, in transit, and during processing is essential to safeguard sensitive information. Organizations should:
- Implement strong encryption standards for data protection.
- Use role-based access control (RBAC) and zero-trust security models to minimize unauthorized access.
- Enforce multi-factor authentication (MFA) to strengthen identity verification.
4. Ensure Regulatory Compliance Through Automated Policies
With GDPR, CCPA, and DPDP Act enforcement tightening globally, compliance must be embedded into data privacy strategies. Organizations can:
- Automate policy enforcement to detect and mitigate compliance risks in real time.
- Conduct regular compliance audits to align with evolving regulations.
- Implement data localization strategies to meet jurisdictional requirements.
5. Strengthen Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Measures
With rising cyber threats like ransomware and insider attacks, enterprises must implement DLP tools that:
- Monitor and restrict unauthorized data transfers across networks.
- Use behavioral analytics to detect anomalies and insider threats.
- Establish automated alerts and remediation workflows for real-time risk mitigation.
6. Implement Secure Data Sharing and Collaboration Practices
Modern enterprises rely on data sharing and cross-border collaboration, but security must not be compromised. Best practices include:
- Enforcing least-privilege access to minimize unnecessary data exposure.
- Implementing secure data-sharing frameworks such as tokenization and anonymization.
- Using audit trails and logging mechanisms to track data movement.
Industry Trends: The Rising Imperative of Data Privacy
- 95% of organizations report that the benefits of investing in data privacy outweigh the costs, with the average enterprise achieving a 1.6x return on their privacy investment.
- 94% of organizations acknowledge that inadequate data protection would drive customers away, emphasizing that strong privacy measures are essential for maintaining trust and business continuity.
- 72% of Americans believe stricter government regulations are needed to control how personal data is collected, used, and shared, reflecting growing concerns over data privacy and consumer protection.
Getting Started with Data Dynamics:
- Read the latest IDC Spotlight Paper – Rethinking Data Security: Improving Privacy and Compliance with a Shared Approach
- Learn about Unstructured Data Management
- Schedule a demo with our team