- Open Finance, fueled by open APIs and cutting-edge technologies, is reshaping the financial landscape, offering unprecedented opportunities for innovation and inclusivity.
- It’s the new era of banking, one that liberates individuals and businesses, allowing secure financial data sharing, challenging the grip of traditional institutions, and ushering in a new era of personalized and convenient financial experiences.
- This transformation has changed our understanding of Data Sharing too. No doubt, the shift towards data openness paves the way for a more inclusive, competitive, and innovative financial ecosystem. However, it comes with challenges, particularly in data security and privacy.
- In the intricate domain of modern data sharing, where vast streams of information flow in diverse formats and structures, the significance of Unstructured Data Management (UDM) emerges as a linchpin for organizations striving for effective and risk-free data utilization.
In the ever-evolving landscape of finance, the significance of data has become the cornerstone of innovation, ushering in a new era that reshapes how information is shared, accessed, and strategically utilized. At the forefront of this data-driven revolution is Open Finance, a framework leveraging open APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) and other technologies to seamlessly share and integrate financial data and services. This stands in stark contrast to the traditional approach, where financial institutions primarily control consumer data.
Within the Open Finance ecosystem, individuals and businesses can securely share their financial data with third-party service providers, dismantling data silos and redefining the concept of Data Sharing. This shift towards data openness paves the way for a more inclusive, competitive, and innovative financial ecosystem. However, it comes with challenges, particularly in data security and privacy.
Enter Unstructured Data Management (UDM), recognized as the linchpin for fostering efficient and secure data sharing practices. UDM becomes the guiding force in navigating the complexities of today’s financial landscapes. In this intricate balance of innovation, challenges, and strategic use of unstructured data, the true potential of finance in the digital age unfolds. Join us as we delve into the depths of this data-centric evolution, exploring how Data Sharing is evolving in the current AI landscape, its implications, regulatory mandates, and how Unstructured Data Management emerges as the key to unlocking unprecedented opportunities while ensuring the security and efficiency of data-sharing practices in the financial realm
The Changing Landscape of Data Sharing in Finance
In the traditional approach to data sharing in finance, financial institutions held the primary control over consumer data. This centralized data model restricted consumer access to their own financial information and limited the ability of third-party providers to develop innovative financial products and services. The lack of data transparency and competition resulted in a less personalized and convenient financial experience for consumers.
Open Finance, also known as Open Banking, represents a transformative shift in data-sharing practices in the financial industry. It breaks down data silos by empowering consumers to securely share their financial data with authorized third-party providers with their explicit consent. This open-data approach fosters innovation and competition, leading to more personalized and convenient financial services for consumers. Several factors are driving this change:
- Technological Advancements: Advancements in cloud computing, APIs, and data analytics have revolutionized banking. No more wait times, communication gaps, multiple follow-ups, or dependencies. Today, it all comes down to just one click. According to a Gartner report, the global cloud computing market is projected to reach $462 billion by 2022, fueling the backbone of secure data sharing and analysis.
- Regulatory Changes: New tech developments bring new rules and guidelines. The rise of AI has opened doors to more sophisticated and frequent cyber attacks, causing substantial harm to consumers and organizations. Regulatory bodies are tightening their grips to prohibit these attacks and ensure enterprises are more proactive than reactive. For instance, regulatory frameworks like PSD2 in the European Union and the Open Banking Standard in the UK have mandated open data-sharing practices. The implementation of PSD2 in the European Union has already influenced a 53% increase in the number of third-party providers offering payment services.
- Consumer Demand: Consumers increasingly demand more personalized, convenient, and cost-effective financial services, but not at the expense of their privacy. They demand more control over their data, explicitly about who, how, and when their data is being used. Beyond convenience, an Accenture study finds that 76% of consumers now prioritize financial institutions that demonstrate ethical business practices.
Navigating the Risks: Cybersecurity, Privacy, and Regulatory Compliance
As Open Finance opens doors to innovation, it concurrently presents a nuanced risk landscape that demands vigilant navigation. Cybersecurity vulnerabilities are heightened as data flows more freely between entities. The interconnected nature of Open Finance ecosystems creates a broader attack surface, necessitating robust security measures. According to a Cybersecurity Ventures report, cybercrime damages are projected to cost the world $10.5 trillion annually by 2025.
Privacy concerns also loom large. As data is shared across a multitude of platforms, ensuring compliance with data protection regulations becomes paramount. Striking a delicate balance between innovation and safeguarding individual privacy rights is a tightrope walk that requires meticulous attention. Regulatory compliance is another dimension of risk. The landscape is evolving rapidly, and financial institutions must stay agile to comply with an intricate web of regulations. Non-compliance not only invites legal repercussions but also erodes the trust of consumers, a cornerstone of Open Finance’s success.
Despite the risks, Open Finance unlocks a myriad of opportunities that transcend traditional boundaries. The democratization of financial services is one of the most notable impacts. Consumers, armed with the ability to securely share their financial data, can now access a plethora of innovative products and services tailored to their specific needs. The rise of fintech startups also exemplifies this transformative wave. These nimble and innovative entities leverage shared data to create groundbreaking solutions, challenging the status quo of traditional banking. Access to a broader spectrum of financial products, streamlined processes, and enhanced user experiences are becoming the norm, all fueled by the collaborative ethos of Open Finance. For instance, the Open Banking Standard in the UK has not only fostered compliance but also inspired a 78% increase in fintech startups aiming to revolutionize financial services.
OECD’s Guidance on Open Finance Data Sharing
In recognition of the transformative potential and inherent risks associated with Open Finance, the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) has developed a comprehensive set of guidelines for Open Finance data sharing. These guidelines aim to promote responsible data-sharing practices and safeguard consumer privacy while fostering innovation and competition in the financial sector.
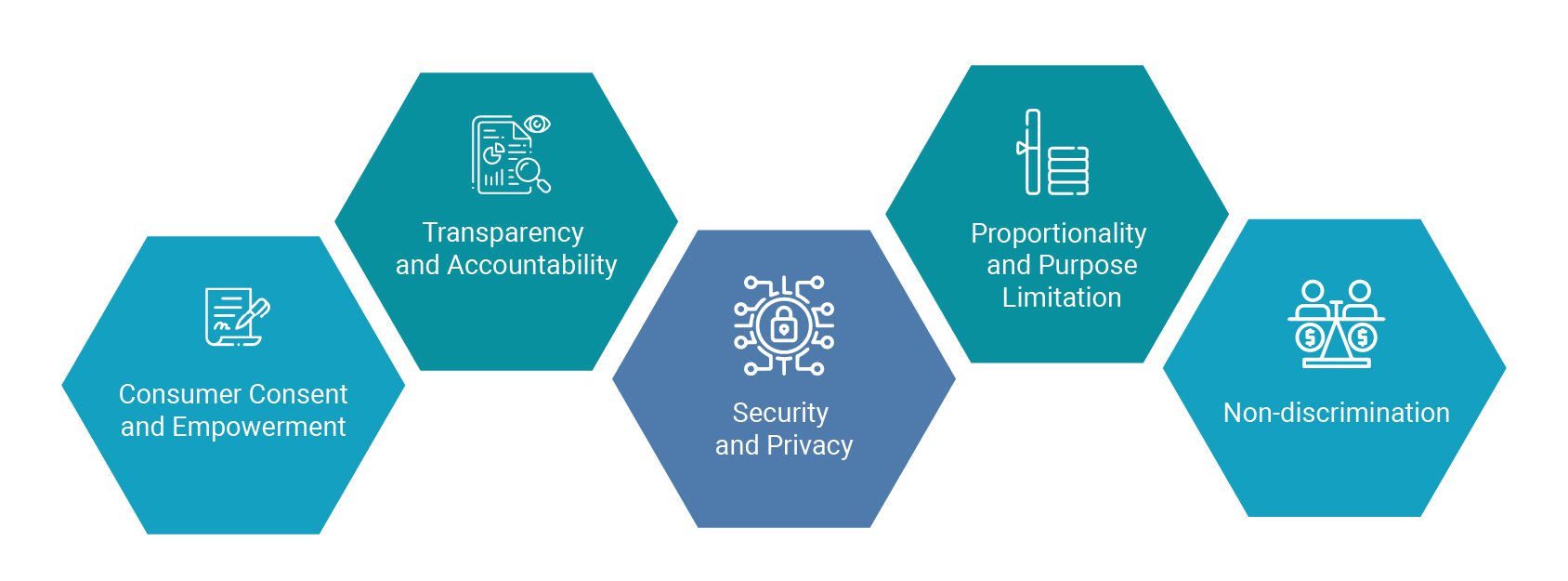

- Consumer Consent and Empowerment: Consumers should have clear control over how their financial data is shared and used. Explicit and informed consent is fundamental to data-sharing practices.
- Transparency and Accountability: Data-sharing practices should be transparent and accountable. Consumers should have clear explanations of how their data is collected, used, and shared, and providers should be held accountable for their data handling practices.
- Security and Privacy: Robust cybersecurity measures and clear data governance frameworks are essential to safeguard consumer data from unauthorized access, misuse, or loss.
- Proportionality and Purpose Limitation: Data sharing should be limited to the purpose for which it is authorized and should not be excessive.
- Non-discrimination: Open Finance data sharing should not lead to unfair discrimination or exclusion. Data-sharing practices should be designed to promote financial inclusion and accessibility.
These principles provide a framework for responsible data-sharing practices in the Open Finance ecosystem, ensuring that consumers’ rights are protected, data is handled securely, and innovation is fostered without compromising consumer trust and privacy. Financial institutions and third-party providers can implement the OECD’s Guidance on Open Finance Data Sharing by adopting the following measures:
- Establish Clear Data Sharing Agreements: Develop clear and comprehensive data sharing agreements that outline the purpose of data sharing, data usage restrictions, consumer consent mechanisms, and data security protocols.
- Implement Strong Data Governance Frameworks: Establish robust data governance frameworks that adhere to the OECD’s principles of transparency, accountability, security, proportionality, and non-discrimination.
- Conduct Regular Data Governance Reviews: Regularly review and update data governance frameworks to ensure they remain aligned with evolving data-sharing practices and regulatory requirements.
- Empower Consumers with Data Control Tools: Provide consumers with easy-to-use data control tools that allow them to manage their data-sharing preferences, access their data, and revoke consent at any time.
- Engage in Open Dialogue with Stakeholders: Foster open dialogue and collaboration with consumers, regulators, and other stakeholders to improve data-sharing practices and address emerging concerns continuously.
The Role of UDM in Ensuring Effective and Secure Data Sharing
In the intricate tapestry of modern data sharing, where vast streams of information flow in diverse formats and structures, the significance of Unstructured Data Management (UDM) emerges as a linchpin for organizations striving for effective and risk-free data utilization. Unlike traditional models that predominantly dealt with structured data neatly housed in databases, the evolving landscape of data sharing now demands a dynamic approach to handle the overwhelming volume of unstructured data residing in emails, documents, multimedia, and various unconventional sources.
Unstructured data poses a unique set of challenges for organizations. Unlike structured data neatly organized in databases, unstructured data lacks a predefined format. It encompasses a broad spectrum of information, including text, images, videos, and more. Its inherent lack of organization and standardized format makes it significantly different from the neatly categorized datasets that businesses are accustomed to managing. This complexity can lead to data silos, hindering the seamless flow of information crucial for effective data sharing practices. Moreover, unstructured data is often characterized by a lack of clear organization and is susceptible to privacy and security risks. The sheer volume of unstructured data further exacerbates the challenge, creating potential bottlenecks in storage, management, and analysis. According to Gartner, unstructured data constitutes a staggering 80% of the total data within an organization.
In the context of consumer data sharing, these challenges become magnified. Consumers entrust organizations with a wealth of personal information, and mishandling this data can result in severe consequences, ranging from privacy breaches to reputational damage.
However, we cannot ignore that while the sheer volume and complexity of unstructured data pose challenges in storage, management, and analysis, they also harbor a wealth of untapped insights crucial for innovation, risk mitigation, and overall business success. Here’s where Unstructured Data Management steps in as a catalyst for efficient and risk-free data sharing. UDM revolves around understanding, organizing, and optimizing unstructured data, unlocking its true potential for organizations while mitigating inherent risks.
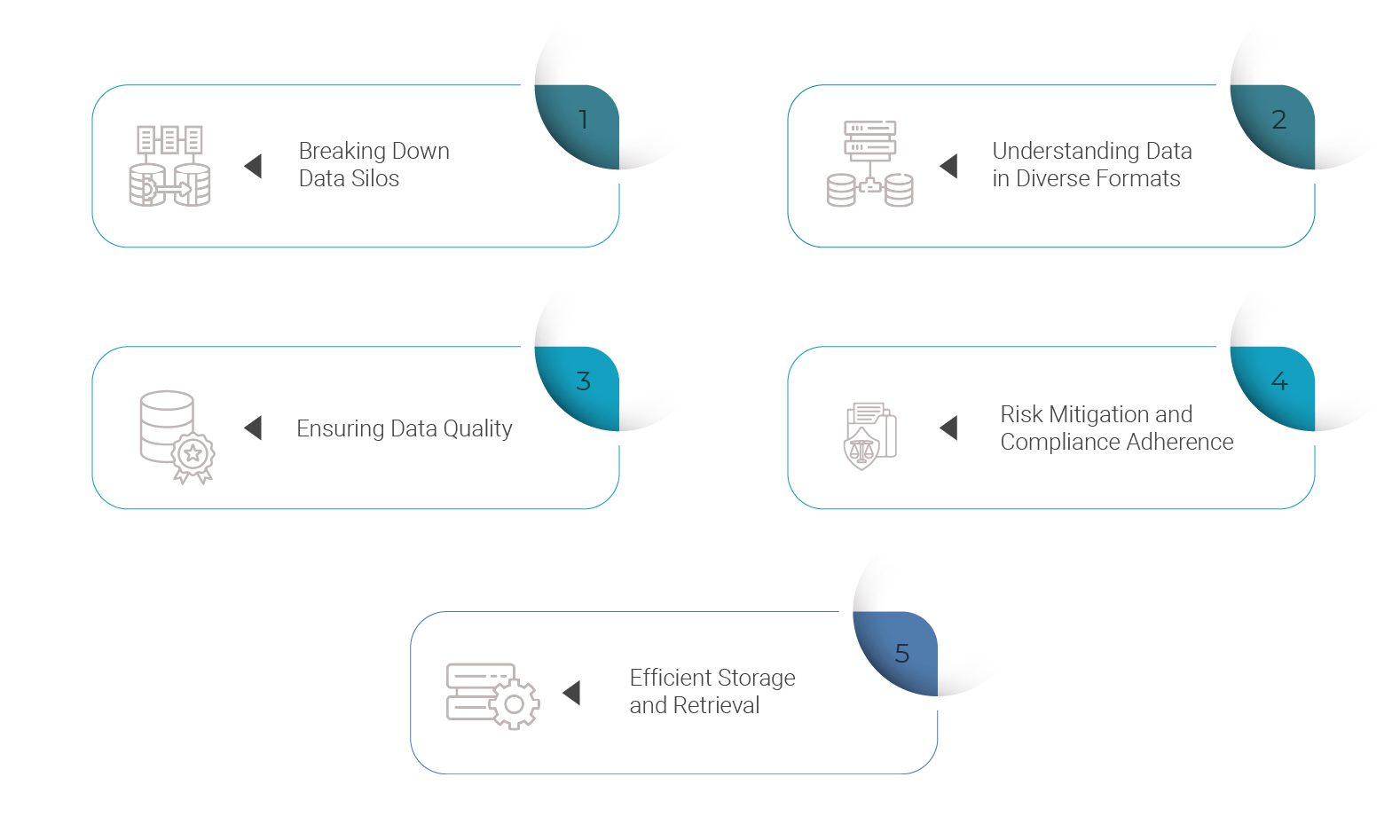

- Breaking Down Data Silos: UDM plays a pivotal role in transforming the seemingly chaotic nature of unstructured data into a structured goldmine. One of its primary advantages lies in breaking down data silos that often hinder seamless sharing and utilization. UDM involves the intelligent categorization and analysis of this data, ensuring that valuable insights are not buried within the unstructured chaos. By creating a unified framework that encompasses both structured and unstructured data, UDM facilitates a holistic understanding of information, enabling organizations to extract meaningful insights. This integration is pivotal for effective decision-making, as it allows for a holistic understanding of data insights, consumer preferences, behaviors, and interactions. According to Gartner, organizations that effectively utilize their unstructured data can achieve up to a 60% cost reduction in data management.
- Understanding Data in Diverse Formats: Traditional data models are adept at handling structured data with predefined categories and fields. However, unstructured data introduces a level of complexity that requires specialized management. UDM excels in understanding and categorizing data in diverse formats, from text and images to audio and video. This nuanced comprehension enables organizations to derive valuable context from seemingly disparate sources, enhancing the depth and richness of the insights extracted. This capability is particularly crucial in the context of consumer sentiment analysis, enabling organizations to gauge and respond to customer feedback effectively. The adoption of advanced analytics tools for unstructured data can result in a 45% increase in the accuracy of sentiment analysis, as reported by Deloitte.
- Ensuring Data Quality: Data quality is a cornerstone of effective decision-making. For instance, one of the key challenges in consumer data sharing is maintaining data quality. Inaccurate or outdated information can lead to flawed insights and decisions. UDM addresses the challenges by incorporating robust data quality management processes, including data cleansing and validation, ensuring that the shared consumer data is accurate, reliable, and up-to-date. Organizations can thereby trust the integrity of the information being shared, mitigating the risks associated with erroneous or incomplete data. According to Experian, 99% of organizations believe that having accurate data is crucial for their business success.
- Risk Mitigation and Compliance Adherence: Data sharing, especially in the context of Open Finance, introduces inherent risks associated with the potential exposure of sensitive information. Consumer data, often subject to stringent privacy regulations, requires meticulous handling to ensure compliance. UDM integrates robust data governance and security measures, mitigating privacy risks associated with unstructured data. This proactive approach not only safeguards consumer information but also ensures adherence to regulatory frameworks, fostering trust and compliance. A survey by PwC indicates that 86% of consumers are concerned about the security of their personal data, emphasizing the need for robust data security measures.
- Efficient Storage and Retrieval: Unstructured data, if left unmanaged, can become a storage nightmare, consuming resources without delivering commensurate value. In a nutshell, data becomes a liability rather than an asset. UDM involves implementing advanced storage and retrieval mechanisms for unstructured data, optimizing the process of accessing relevant information. This efficiency is critical in scenarios where prompt access to consumer data is essential, such as customer service interactions or personalized marketing campaigns. According to IDC, organizations that implement efficient storage solutions for unstructured data can achieve a 30% reduction in storage costs.
As Open Banking and subsequent data sharing evolves, UDM emerges not just as a solution but as a strategic imperative for organizations aiming to navigate the intricacies of information exchange effectively. It’s a paradigm shift from viewing unstructured data as a challenge to embracing it as a valuable asset.
The Data Dynamics Advantage
In the intricate landscape of modern data sharing, where the sheer volume and diversity of information pose significant challenges, Data Dynamics emerges as a key player in facilitating secure and efficient data sharing. The finance sector, in particular, grapples with colossal volumes of unstructured data—approximately 80% of its data—making the need for an effective data management solution crucial. Data Dynamics steps into this space with its Unified Unstructured Data Management Platform, providing a holistic approach to address the complexities of unstructured data and, in turn, fostering secure and efficient data sharing practices.
At the core of Data Dynamics’ solution is its Unified Unstructured Data Management Platform, a comprehensive offering that seamlessly integrates various technologies, including automation, artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and blockchain. Trusted by over 28 Fortune 100 organizations, this platform is designed to adapt to the demands of global enterprise workloads, ensuring scalability and efficiency.
One of the platform’s pivotal modules is Content Analytics, which harnesses the power of Data Science Engine, AI/ML, and Natural Language Processing (NLP) for for accurate discovery and classification of data. This capability enables organizations to understand the sensitivity, consumer information, and business value of their data. Risk Exposure Insights, another feature of Content Analytics, empowers organizations with actionable insights through descriptive and diagnostic analytics, offering a comprehensive understanding of potential risks. This level of visibility is essential for making informed decisions regarding data sharing practices. Data Dynamics prioritizes data security and compliance, recognizing the sensitive nature of financial data. The platform provides robust security measures, including risk remediation and access control, to ensure that high-risk sensitive data is quarantined in secure storage. This not only enhances data security but also facilitates compliance with stringent regulatory frameworks governing the finance sector. The Open Share Reporting functionality further enhances security by identifying sensitive data within open shares and rectifying permissions accordingly, ensuring that data is shared with the right individuals or entities.
Ultimately, Data Dynamics envisions a future where financial institutions achieve data democratization. This vision translates into users of varying technical backgrounds swiftly accessing, comprehending, and extracting maximum insights from sprawling unstructured data landscapes. It represents a shift from data being a siloed resource to a democratized asset accessible to all relevant stakeholders. In a landscape where the effective management of unstructured data is a competitive advantage, Data Dynamics stands as a strategic partner for financial institutions, offering not just a solution but a transformative approach to data management that aligns with the evolving needs of the finance sector.
To explore how Data Dynamics can assist your enterprise in organizing unstructured data and driving secure and efficient data sharing, visit our offerings at www.datadynamicsinc.com or reach out to us at solutions@datdyn.com or (713) 491-4298.